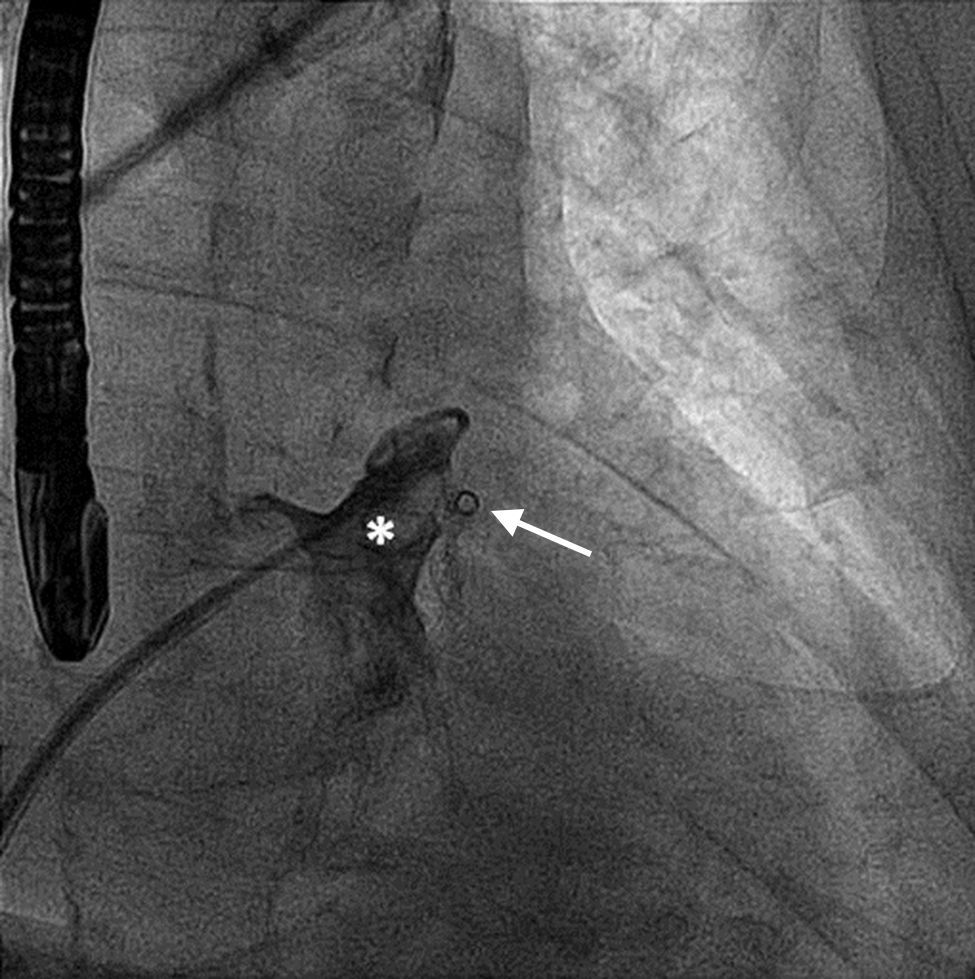
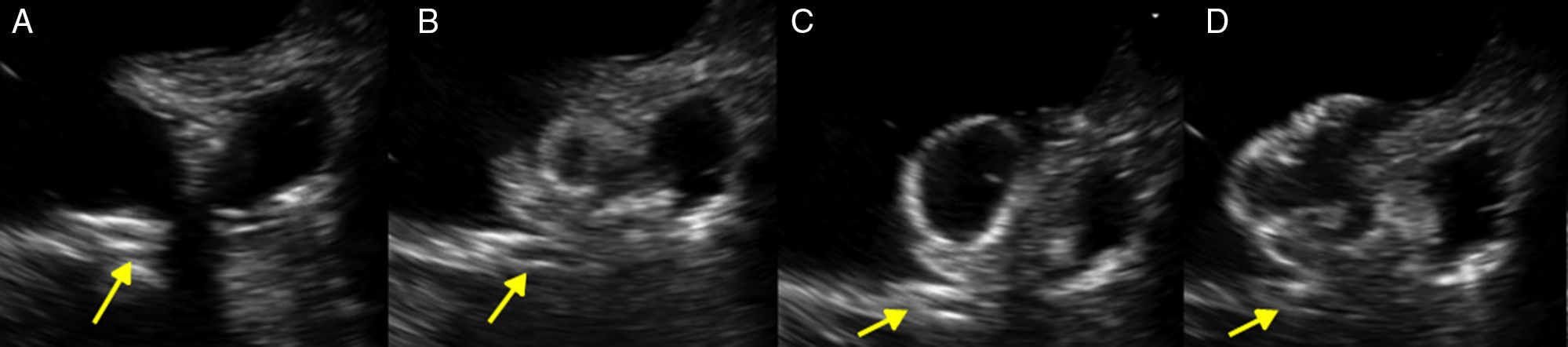
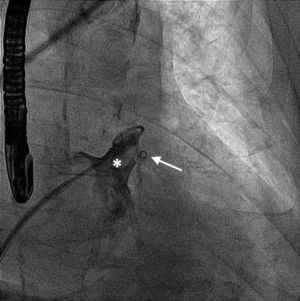
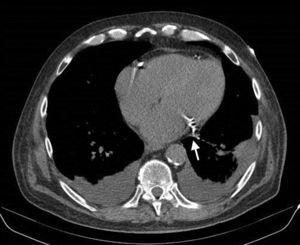
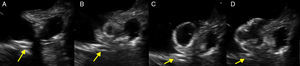
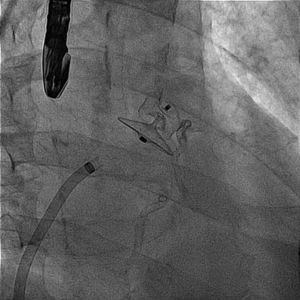
A 61-year-old man, with a history of coronary heart disease and percutaneous coronary intervention, with stents in the right coronary and circumflex arteries, was referred to our center for left atrial appendage (LAA) closure. He had atrial fibrillation with high thromboembolic risk (CHA2DS2VASc=4) and oral anticoagulation was formally contraindicated because of recurrent severe bleeding. Selective angiography of the LAA (Video 1) showed a close relationship between the LAA (Figure 1, asterisk) and the circumflex artery (Figure 1, arrow), well defined by the previously implanted stents. A computed tomography scan performed after a previous episode of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage showed similar findings (Figure 2, arrow). A 22-mm Amplatzer Amulet device was successfully placed, with no residual leak. Intraoperative monitoring by transesophageal echocardiography and post-procedural radioscopy confirmed the close relationship between the device and the circumflex artery (Figures 3 and 4, Videos 2 and 3), which is vital to keep in mind in order to prevent complications during the procedure.
After the Amplatzer was completely deployed, radioscopy confirmed the relationship between the distal lobe of the device and the coronary artery. Although in this patient this latter structure was easily delineated by the previously implanted stents, it is vital to consider this anatomical relationship during the occlusion procedure.
LAA closure is a safe and effective intervention used to prevent stroke and systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation and contraindications for oral anticoagulation. Nevertheless, there may be procedure-related complications such as device embolization and left atrial wall perforation. The close relationship between the LAA and circumflex artery place this latter structure and its branches (including the sinus node artery in 30% of patients) at risk during the procedure. This condition must be considered if the patient develops atrial arrhythmias or signs of myocardial ischemia during the procedure.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.