Endomyocardial fibrosis (EF) is characterized by marked endocardial thickening of the apex and subvalvular apparatus of one or both ventricles. It is considered a primary and chronic form of restrictive cardiomyopathy (the acute form is Löffler's disease) and is associated with inflammation and hypereosinophilia secondary to chronic processes such as parasite infection or autoimmune disease.
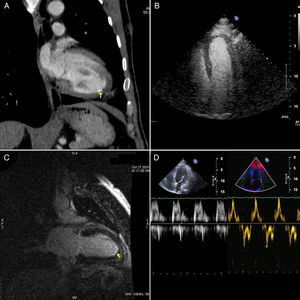
We describe the case of a 38-year-old Guinean man who was admitted to the Internal Medicine department for left upper quadrant pain. He had a previous history of malaria. Physical exam revealed a 4-cm hepatomegaly with tenderness in the epigastrium and hypochondrium without signs of heart failure. The hemogram showed marked eosinophilia (29500/mm3) and loa loa microfilariae were identified in the blood circulation. Thoraco-abdominal CT confirmed hepato- and splenomegaly and showed mild calcification in the left ventricular apex (Figure 1A, arrow). Given the suspicion of EF, the patient was referred for echocardiographic assessment (Figure 1B). Contrast echo revealed no suspicion of restrictive cardiomyopathy, the left ventricle was normal in size and systolic and diastolic function were both normal, with normal filling pressures (Figure 1C). Finally, on cardiac MRI subendocardial late gadolinium hyperenhancement was observed in the left ventricular apex (Figure 1D, arrow), reflecting myocardial fibrosis. The patient's clinical context supports the diagnosis of an initial stage of EF. Cardiac MRI is a very useful tool for the diagnosis of EF as it enables characterization and quantification of fibrous tissue, which has prognostic value.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.