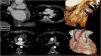
We present two illustrative cases with cardiac computed tomography (CT) findings following coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) using saphenous vein grafts (SVGs) and a venous external support (VEST) device.
The first case shows complete thrombosis of an SVG entirely contained within the VEST device, documented one year after surgery (Figure 1, Panel A). The second case demonstrates severe stenosis at the origin of a radial artery graft to the second obtuse marginal branch and at the origin of an SVG to the right coronary artery. Additionally, there is marked thinning and a significant reduction in the graft's lumen within two VEST-supported sequential bypasses (Figure 1, Panel B).
Panel A: Coronal and axial computed tomography (CT) image and three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction showing complete thrombosis of the circumflex artery, fully contained within the VEST device. Panel B: Axial CT image and 3D reconstruction showing severe stenosis at the origin of a radial artery graft to the second obtuse marginal branch and at the origin of an SVG to the right coronary artery. Additionally, there is a marked thinning and a significant reduction in the graft's lumen within two VEST-supported sequential bypasses.
The VEST device was developed to enhance SVG durability by limiting graft dilation and reducing intimal hyperplasia. However, clinical studies have shown mixed results, with patency rates comparable to those of unsupported SVGs.
These cases illustrate the utility of cardiac CT for structural and functional evaluation of externally supported grafts. While a direct causal relationship between the VEST device and graft failure cannot be established,1–4 imaging highlights the complexity of long-term graft surveillance and the need for individualized assessment.
We contribute uncommon examples to the literature with detailed imaging and late follow-up, which may help expand understanding of the behavior of externally supported venous grafts in clinical practice.
Ethical approvalThe author of this manuscript hereby declares that all research procedures involving human participants were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from the participant included in the study.
Conflicts of interestThe author has no conflicts of interest to declare.