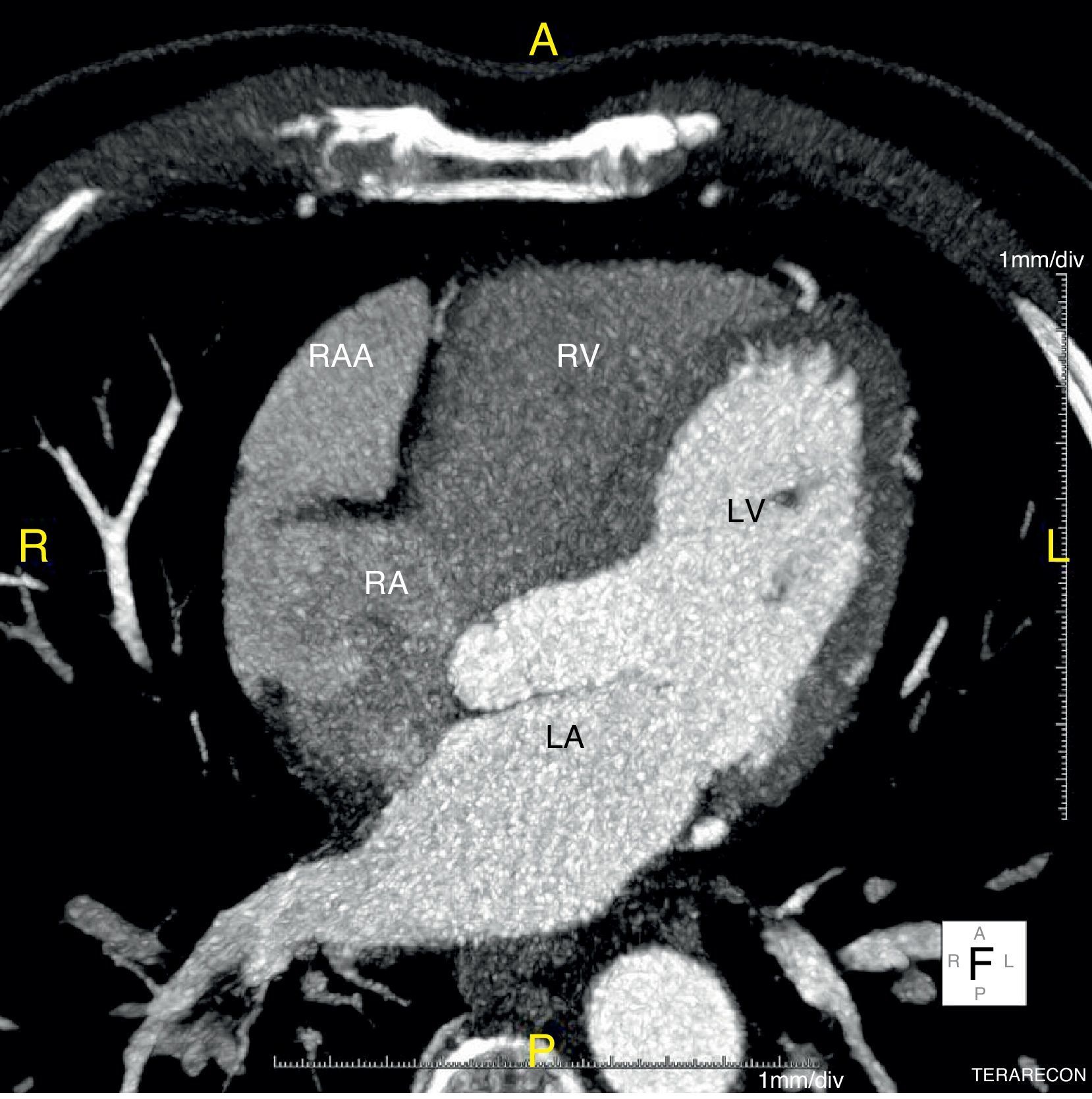
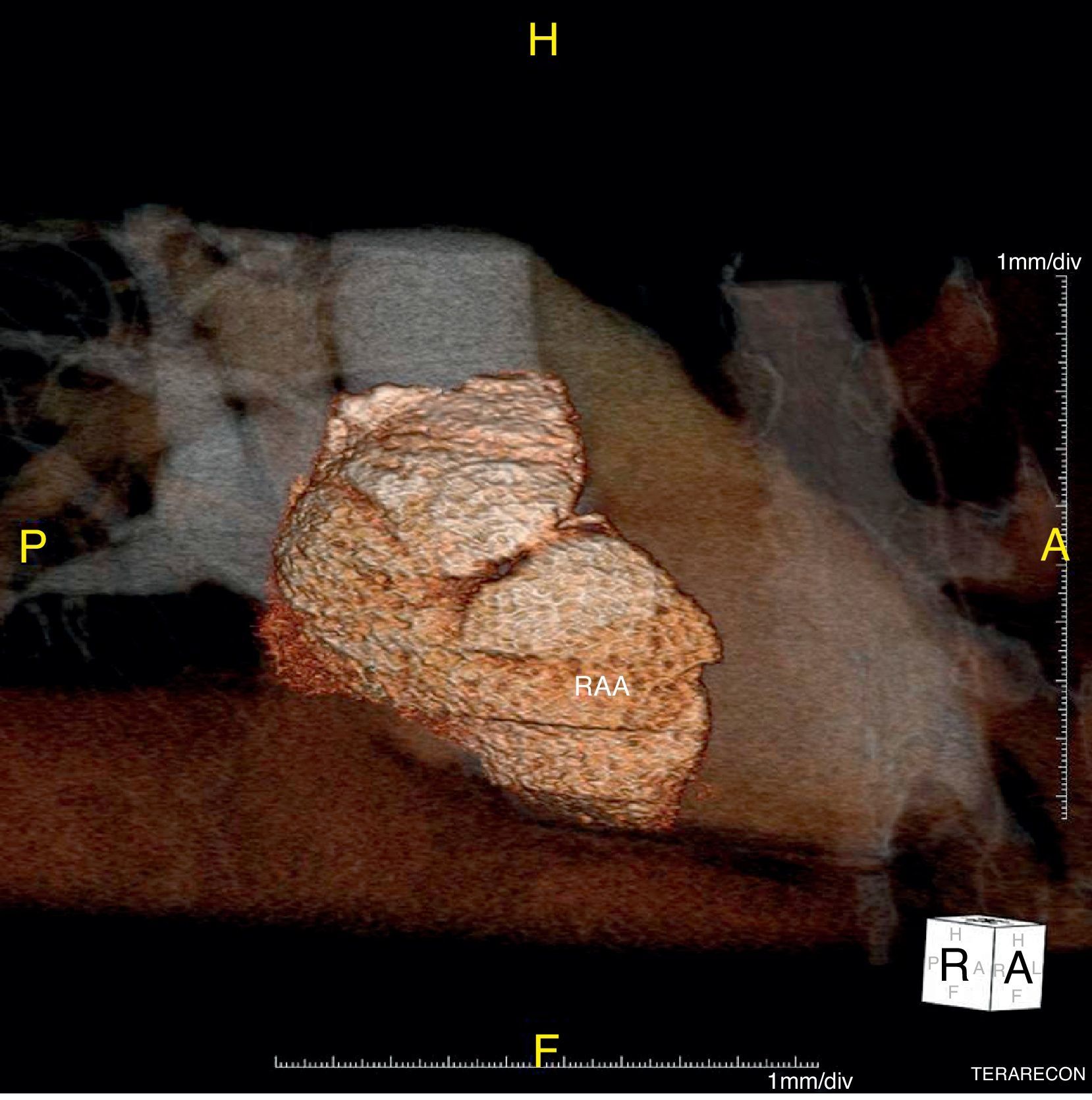
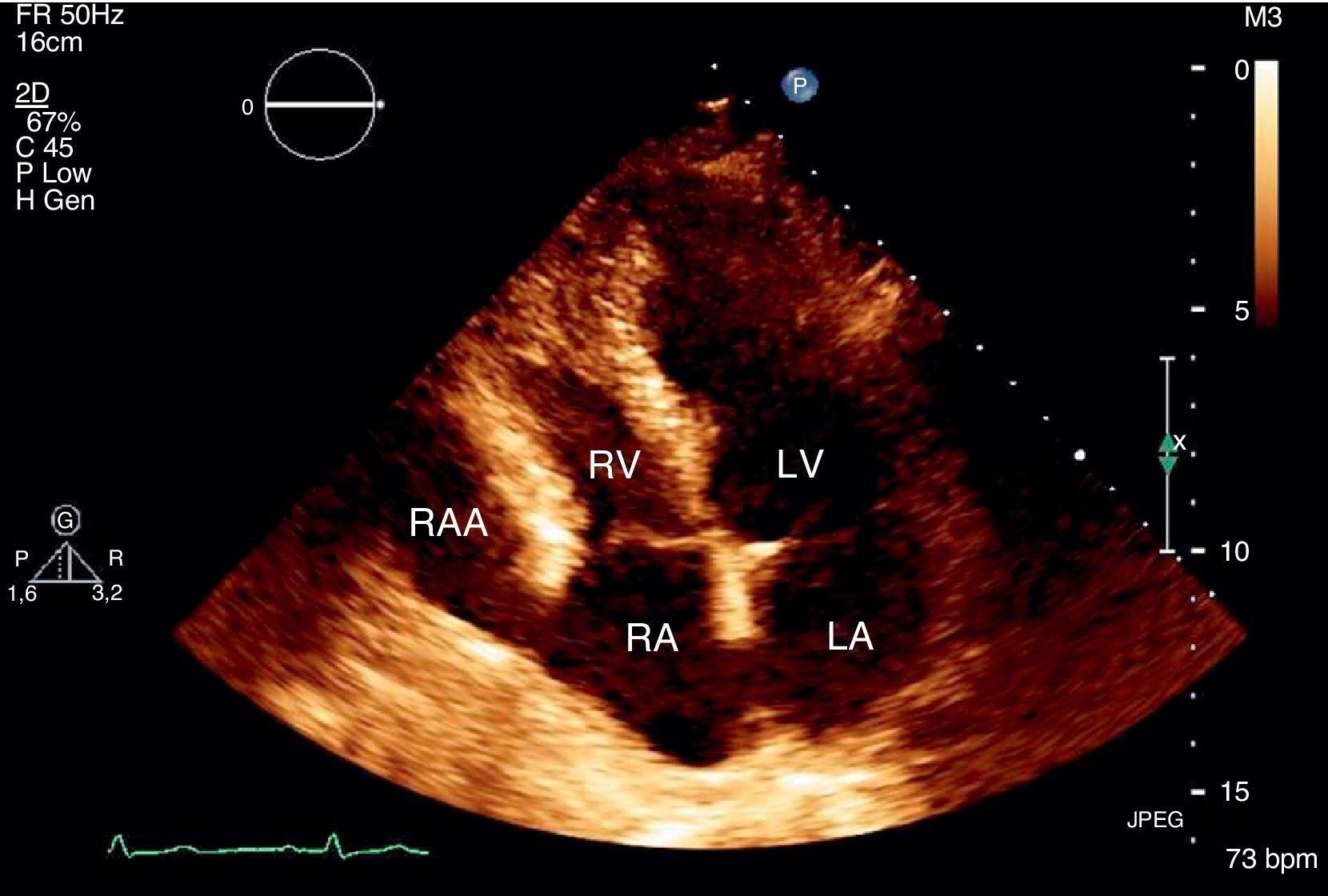
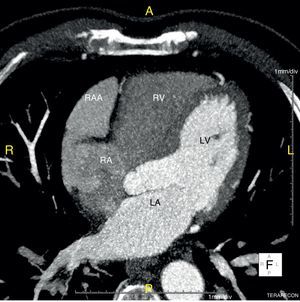
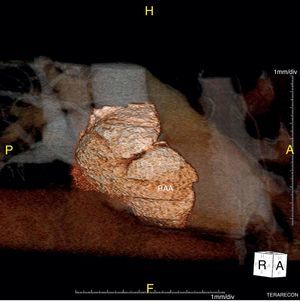
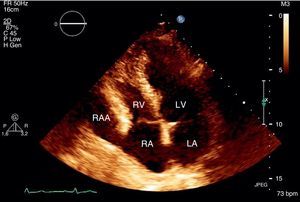
We report the case of a 58-year-old hypertensive man referred for a cardiology consultation due to atypical chest pain. The clinical examination was unremarkable. An electrocardiogram demonstrated sinus rhythm and incomplete right bundle branch block. He had an ambulatory echocardiogram that was described as normal. An exercise test was negative for ischemia and showed intermittent complete right bundle branch block. To exclude coronary disease a contrast computed tomography (CT) scan was performed that revealed a saccular aneurysm of the lateral free wall of the right atrium measuring 45 mm×45 mm×43 mm (Figures 1 and 2). There was no evidence of coronary disease. Given the CT findings, transthoracic echocardiography was repeated and revealed a cystic, pulsatile structure in continuity with the free wall of the right atrium through a narrow neck (Figure 3) permitting low-speed two-way flow, subsequently confirmed by injection of Sonovue® contrast. No cardiac thrombi were visualized. The tricuspid valvular apparatus and right ventricle were morphologically normal, as was biventricular systolic function. Similar findings were visualized on the transesophageal echocardiogram.
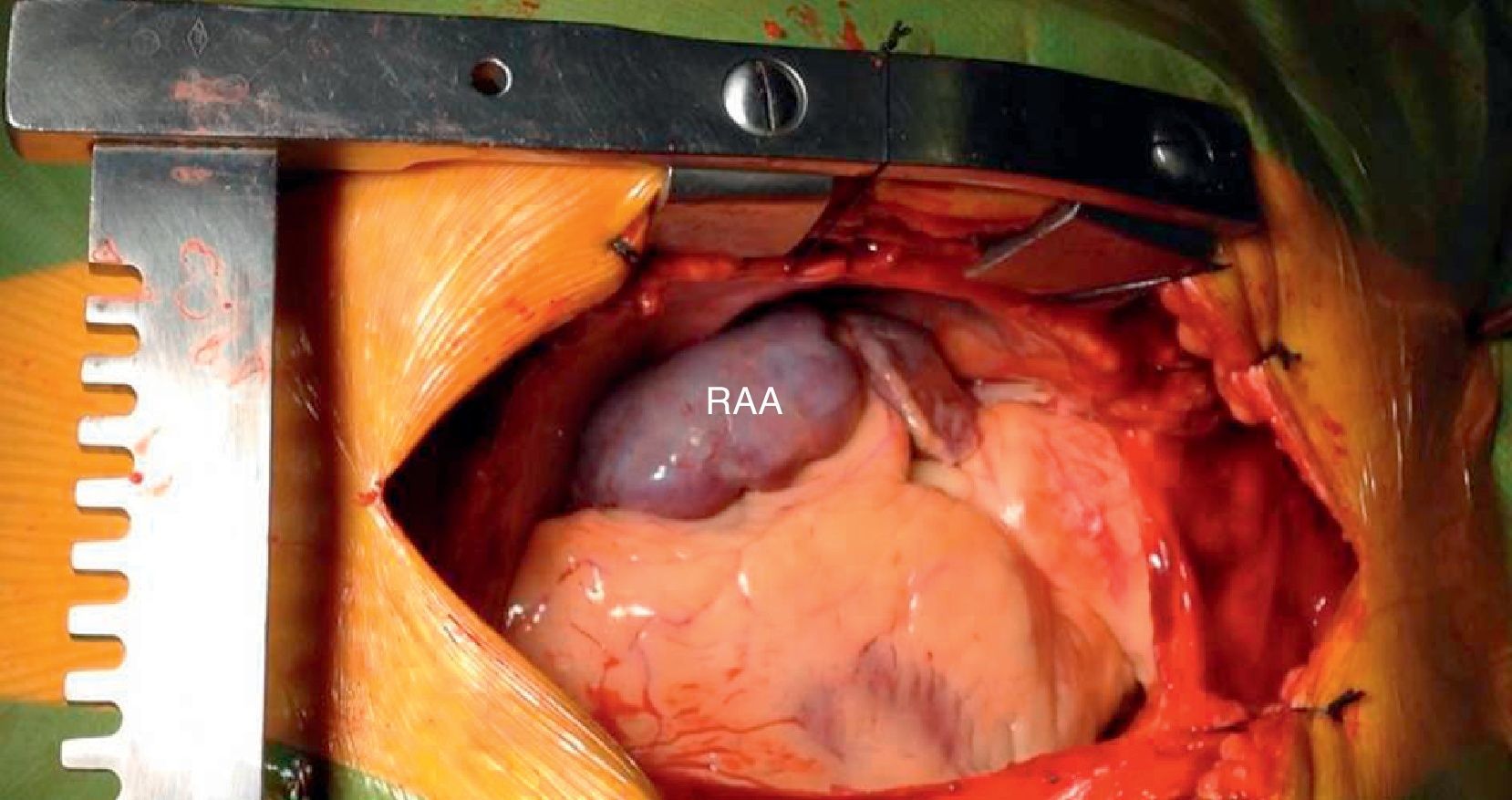
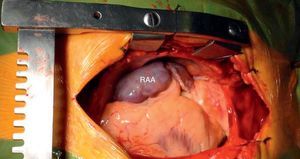
Right atrium aneurysm is a rare congenital heart malformation. It occurs in all age groups. Supraventricular arrhythmias and embolic events are the most common reported symptoms. Major complications such as rhythm disturbances, thromboembolic events and aneurysm rupture may occur. Although the best treatment, particularly in asymptomatic patients, has not been established, the patient was started on oral anticoagulation and proposed for surgical aneurysmectomy. He underwent successful resection of the aneurysm (Figure 4) with an uneventful post-operative period.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the written informed consent of the patients or subjects mentioned in the article. The corresponding author is in possession of this document.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.