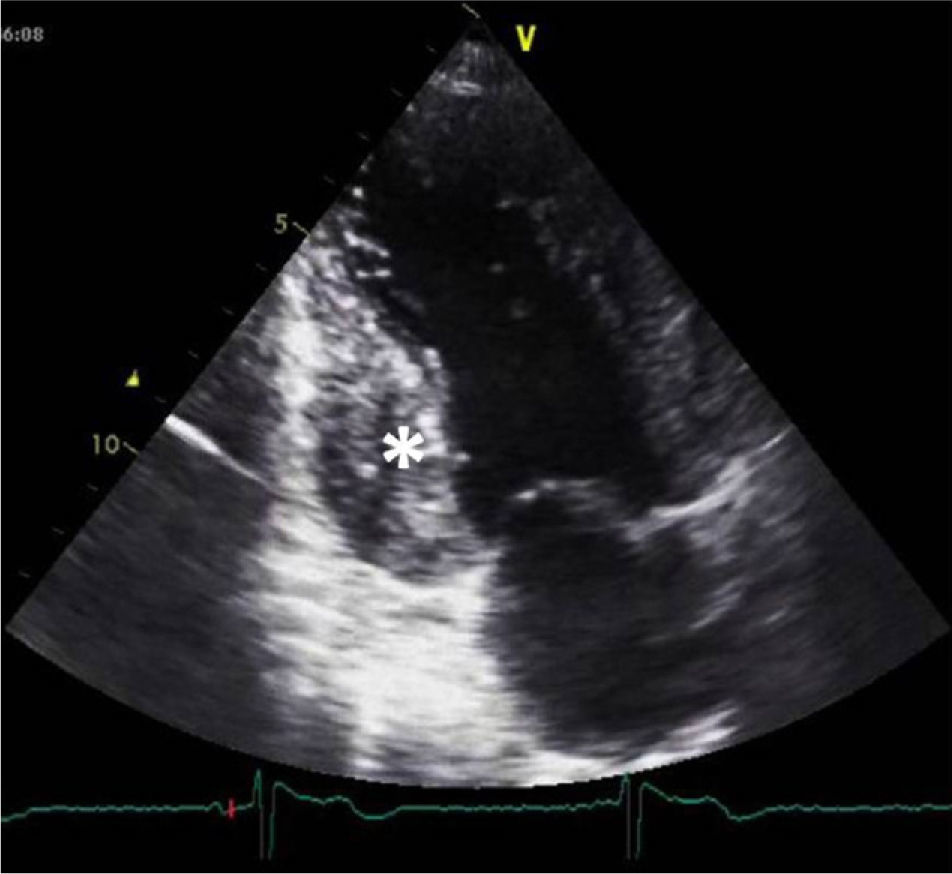
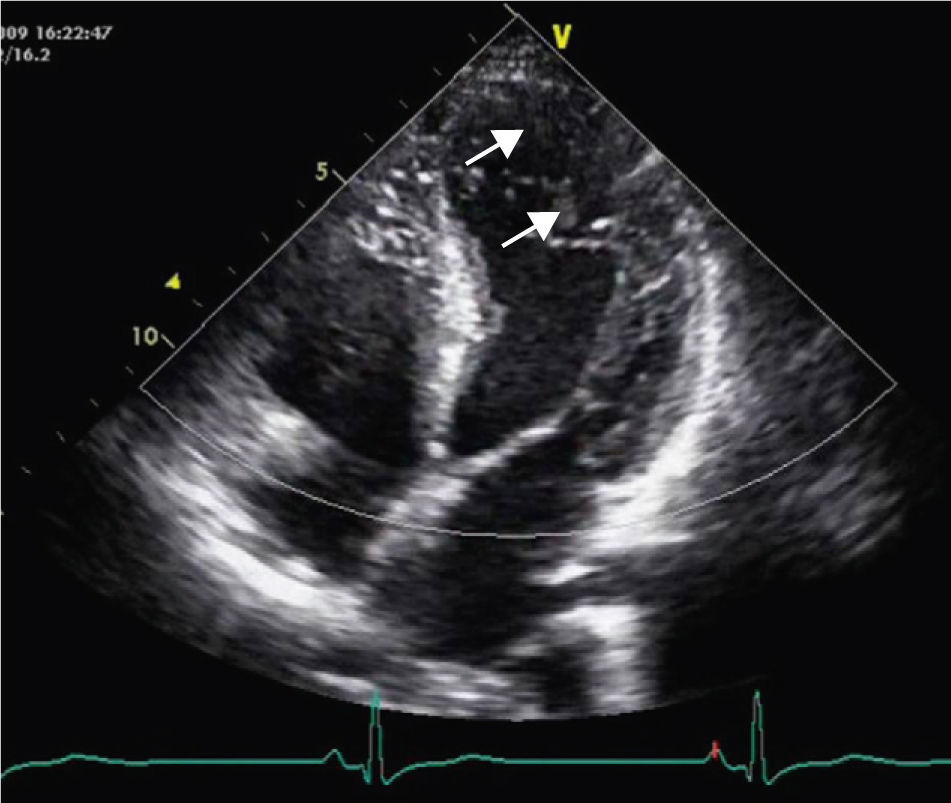
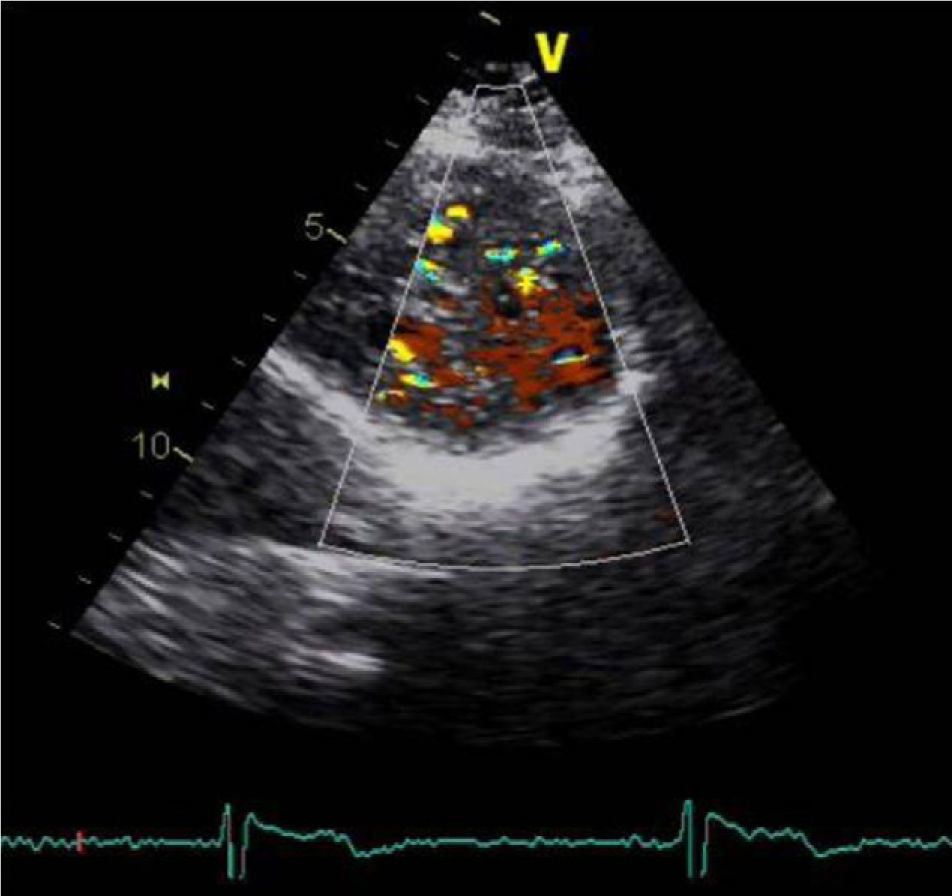
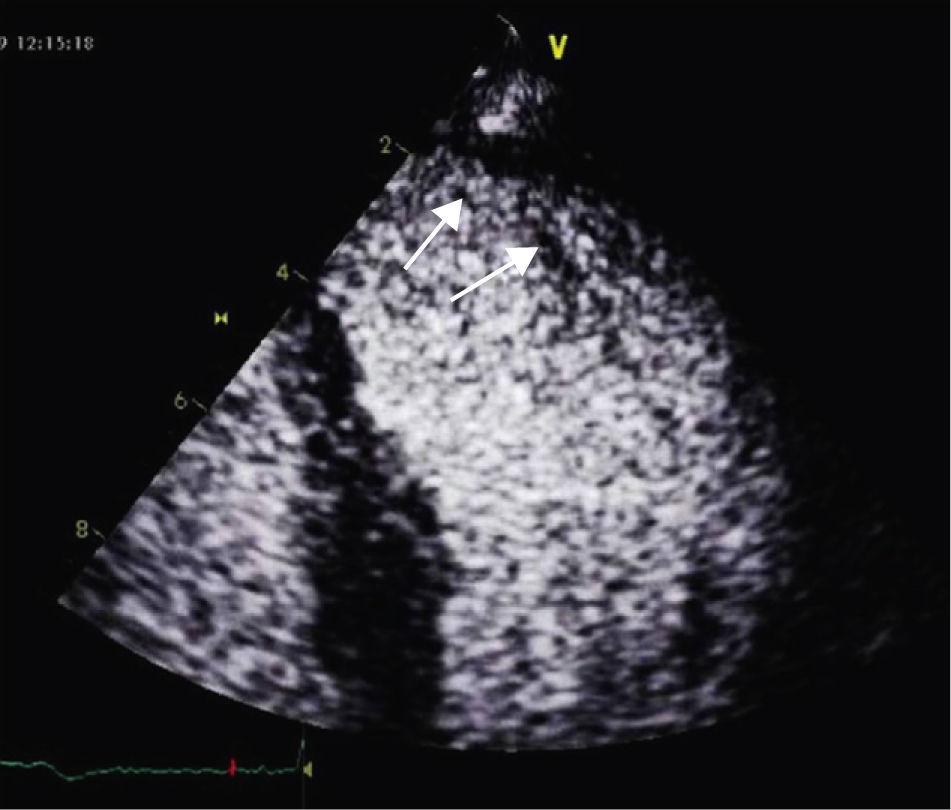
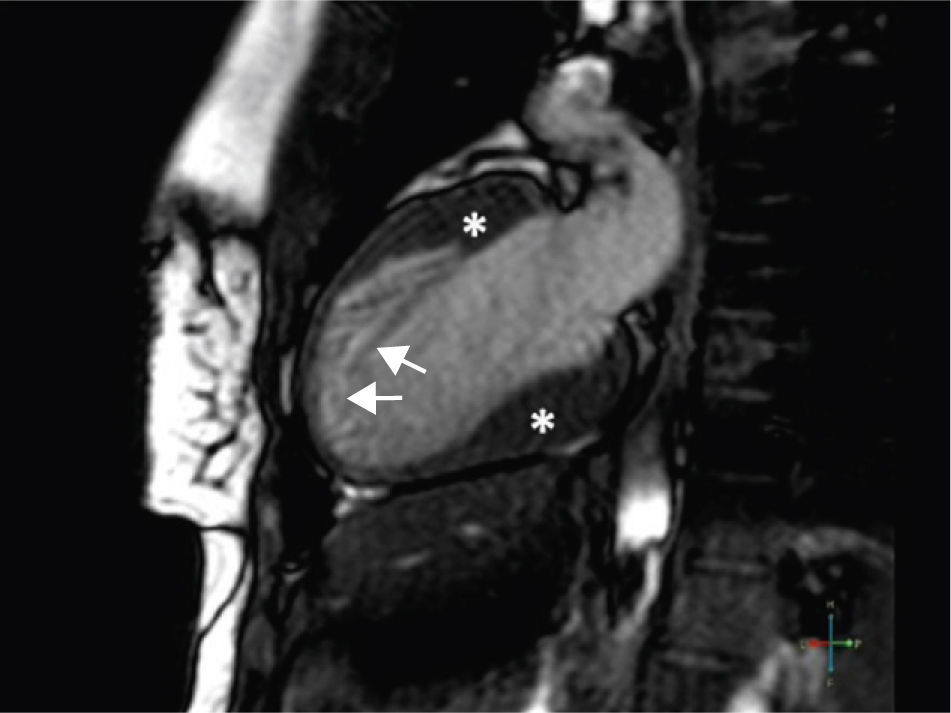
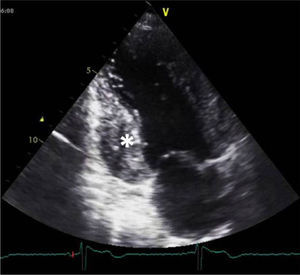
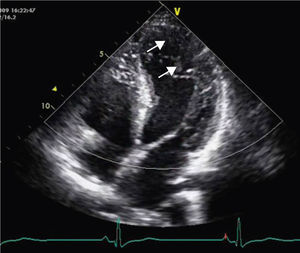
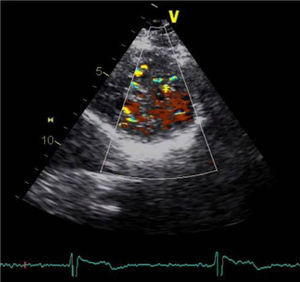
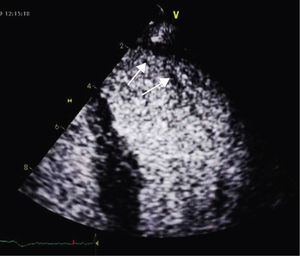
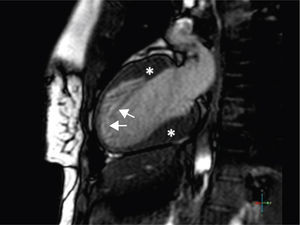
A 34-year-old woman with a history of smoking was observed for rapid palpitations of 12 years’ evolution. The symptoms occurred daily and were of short duration and not associated with dizziness, syncope or chest pain. She had no family history of sudden death, but her father had been diagnosed with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. In the course of assessment she underwent electrocardiography, which revealed sinus bradycardia (36bpm), criteria of left ventricular hypertrophy, abnormal R-wave progression in the precordial leads, nonpathological Q waves, nonspecific alterations in ventricular repolarization in DII, DIII, aVF and V3–V6, and long QTc. Echocardiography showed undilated cardiac chambers and good biventricular systolic function. The left ventricle (LV) presented nonobstructive hypertrophy of the basal segments of the anterior and inferior septum and inferior wall (Figure 1), with a maximum thickness of 21 mm. Hypertrabeculation was observed at the apical level, particularly in the posterior and lateral wall segments (Figures 2 and 3). The ratio of noncompacted to compacted layers was 2.3, measured in parasternal short-axis view at end-systole. Injection of contrast showed myocardial noncompaction at the apical level (Figure 4). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), performed to characterize the cardiac morphology in more detail, confirmed the presence of asymmetric LV hypertrophy associated with LV noncompaction (LVNC) (Figure 5), with a ratio of noncompacted to compacted layers of 3.3, measured at end-diastole. MRI also revealed multiple areas of delayed enhancement in the hypertrophied segments. Holter monitoring did not record any clinically significant arrhythmias and exercise testing showed normal blood pressure changes. The patient's symptoms disappeared after initiation of therapy with bisoprolol. Echocardiographic study of relatives was negative for both hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and LVNC. Genetic study identified the mutation G1505A in exon 17 of the MYBPC3 gene, which results in an amino acid substitution at position 502 of the protein (Arg502Gln).
HCM is the most common genetic heart disease, with a prevalence of 1:500. Transmission is autosomal dominant and over 900 mutations have been identified in 11 genes encoding sarcomeric proteins.1 LVNC is a rare cardiomyopathy with a prevalence of less than 1:5000 and is genetically heterogeneous. The case presented meets the echocardiographic criteria of Jenni et al., and the MRI criteria of Petersen et al. for LVNC,2 which, like HCM, is associated with sudden death. Various mutations that have previously been identified in patients with HCM, including the one found in this case, have been found in patients with LVNC but without HCM.3 There is no information available on the prognostic significance of this mutation. The present case is unusual in that both cardiomyopathies were present in the same patient and the mutation identified may be responsible for both LVNC and HCM.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Please cite this article as: Faria, R, et al. Um doente, uma mutação e duas miocardiopatias – miocardiopatia hipertrófica associada a não compactação do ventrículo esquerdo. Rev Port Cardiol. 2012. doi:10.1016/j.repc.2012.02.004