A 53-year-old man, with a 15-year history of mycosis fungoides (MF), presented with fever, dizziness, and presyncope. On examination, he was tachycardic (180 bpm) and hypotensive (100/70 mmHg). The ECG showed diffuse ST-segment depression, and cardiac troponin I was elevated (3.47 ng/ml). He was admitted with a suspected acute coronary syndrome.
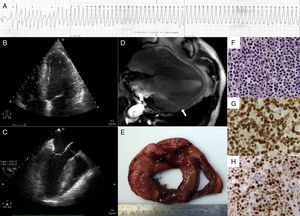
On the third day of hospitalization there were several episodes of sustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia (MVT) (Figure 1A). Electric cardioversion was performed, and intravenous amiodarone was prescribed. On the following days episodes of nonsustained MVT with similar morphology were documented. Transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography showed left ventricular (LV) concentric hypertrophy and diffuse hypokinesia (Figure 1B and C). Coronary angiography revealed no coronary artery disease. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging revealed a mass infiltrating the pericardium and LV myocardium (Figure 1D, arrow).
(A) Telemetry tracing showing monomorphic ventricular tachycardia; (B) transthoracic echocardiogram revealing left ventricular (LV) concentric hypertrophy; (C) transesophageal echocardiogram showing LV concentric hypertrophy; (D) cardiac magnetic resonance imaging revealing infiltration of the myocardium and pericardium (arrow); (E) diffuse myocardial infiltration on macroscopic post-mortem examination; (F) histologic examination (hematoxylin & eosin, ×200) revealing infiltration of the myocardium by lymphocytes; (G) histologic examination (CD3, ×200) showing CD3-positive lymphocytes; (H) histologic examination (Ki-67, ×200) revealing a high proliferative index.
On the fifteenth day of hospitalization the patient had several episodes of sustained MVT, requiring electric cardioversion. A few hours later cardiac arrest with asystole occurred, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation was unsuccessful.
Macroscopic post-mortem examination revealed diffuse myocardial infiltration (Figure 1E) and histological analysis confirmed infiltration by T-cell lymphoma (Figure 1F), with positive CD3 (Figure 1G) and elevated Ki-67 (Figure 1H), corresponding to MF stage IVB.
MF is the most common cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. In advanced stages it can present nodal, visceral, or blood involvement. Cardiac involvement is rare and usually diagnosed incidentally at autopsy, as most patients have no suggestive signs or symptoms. This case demonstrates that cardiac involvement by MF may rarely manifest as MVT.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.