Persistence of the left superior vena cava occurs in about 0.3-0.7% of the general population. It is of particular importance in patients who need cardiac resynchronisation therapy. We present a unique case in which a snare system and tunnelling tool were used to place the left ventricular lead in a patient with persistence of the left superior vena cava.
A veia cava superior esquerda persistente ocorre em 0,3-0,7% da população geral e é de particular importância em doentes que necessitam de terapêutica de ressincronização cardíaca. Apresentamos um caso único onde foram usados um sistema de snare e tunelizador para a implantação do elétrodo esquerdo num doente com veia cava superior esquerda persistente.
Persistence of the left superior vena cava (PLSVC) occurs in about 0.3-0.7% of the general population. It is an anatomic variant of particular importance in patients who need cardiac resynchronisation therapy.
Case reportThe patient was a 77-year-old male with ischaemic heart disease, on ambulatory NYHA IV, depressed left ventricular (LV) function (ejection fraction of 20%) and left bundle branch block (QRS width of 170 msecs), on optimised medical therapy. PLSVC was identified during an attempted left-sided CRT-D implantation at another institution. Cardiac magnetic resonance confirmed the diagnosis of PLSVC with anastomosis to the coronary sinus (CS) ostium. Right-sided CRT-D implantation was then performed with successful placement of the right atrium and right ventricular apical defibrillator leads, although with LV lead implantation failure. The patient was therefore referred to our department for LV lead placement.
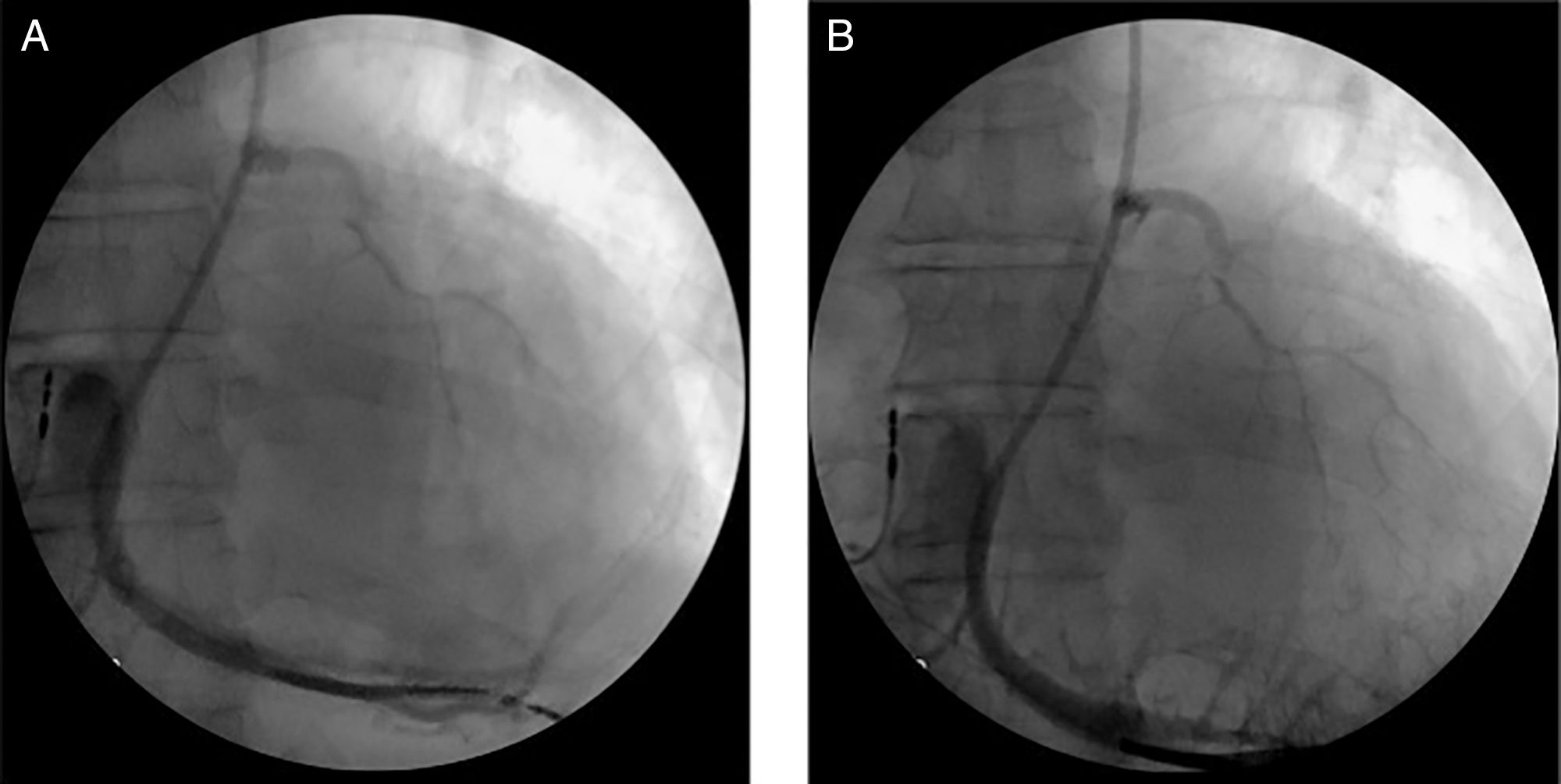
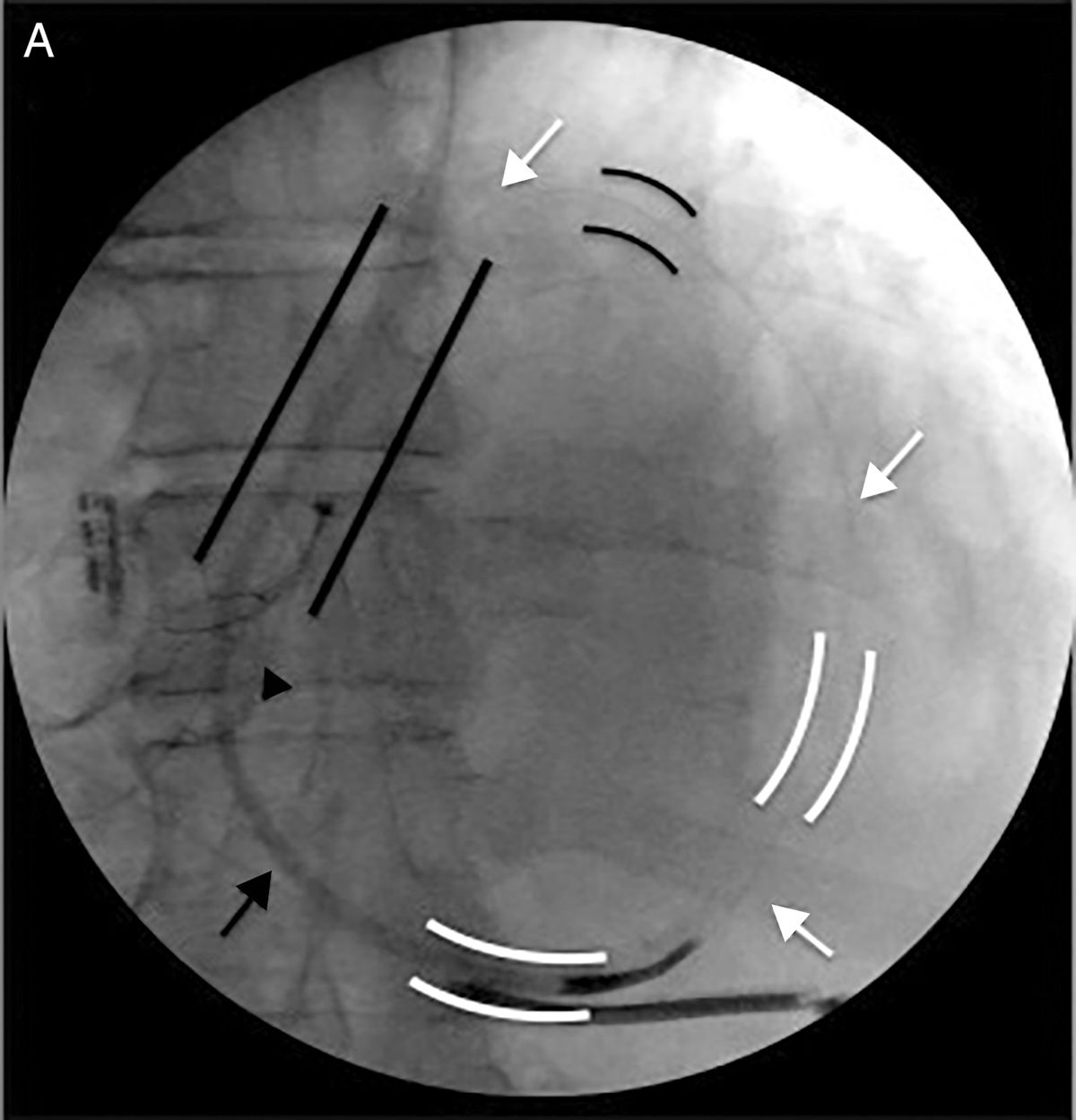
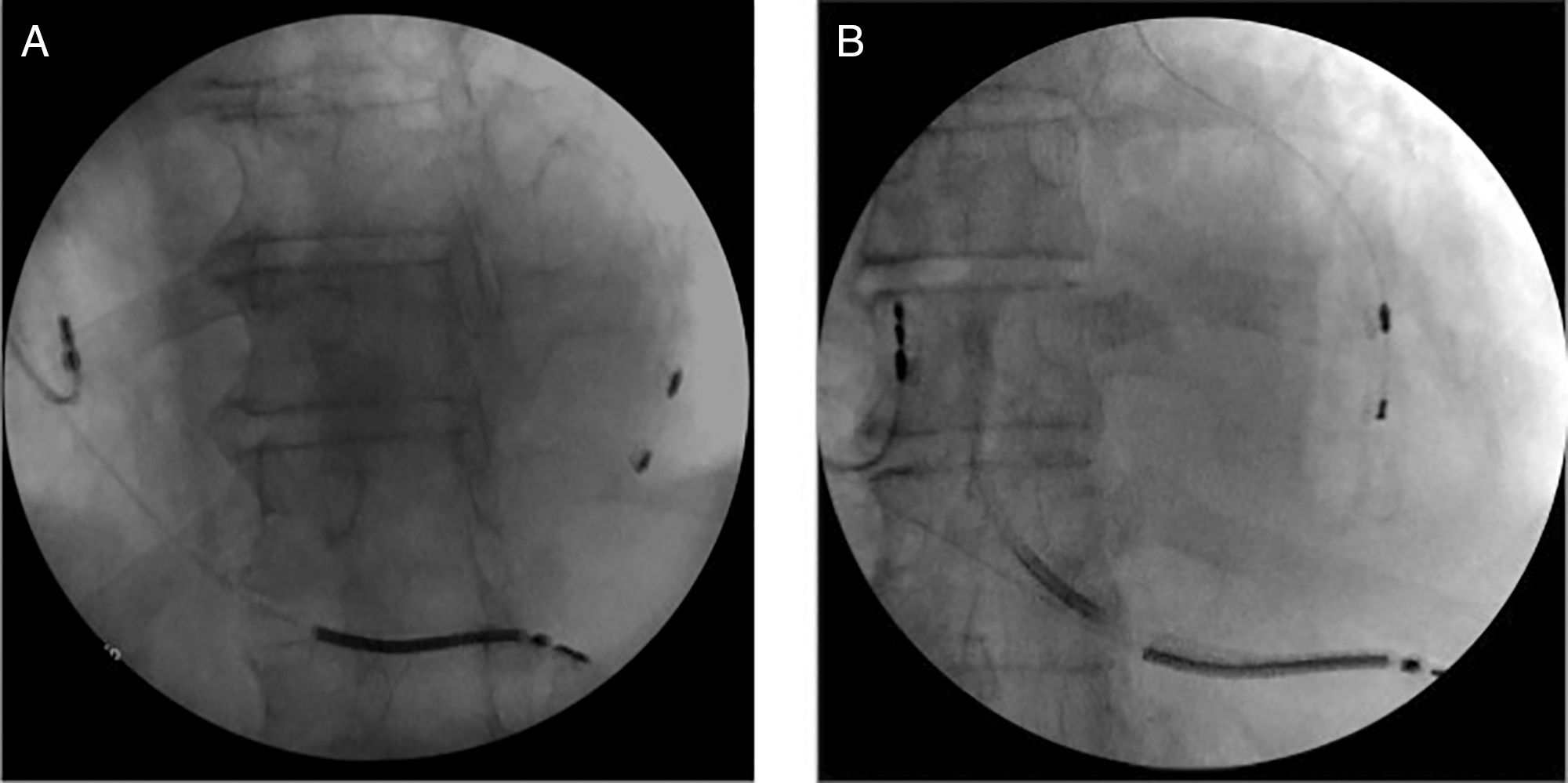
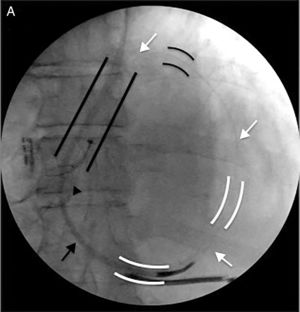
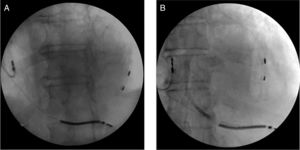
The left subclavian vein (LSV) was punctured for percutaneous sheath insertion. The sheath was advanced through the PLSVC to the CS and venography was performed (Figure 1A and B), followed by selective cannulation of the posterior cardiac vein (Figure 2, black arrow). A guide wire (Acuity Whisper®, Boston Scientific, Inc.) was introduced and advanced through the anterior collateral veins and the anastomotic vein directly back to the PLSVC (Figure 2, white arrow). A snare system (En Snare 30®, Merit Medical Systems, Inc.) was introduced through a second sheath via the LSV up to the PLSVC (Figure 2, black arrow), and the distal end of the guidewire was gradually pulled towards the skin surface. Both ends of the guidewire were under the operator's control. The LV lead was advanced in an antidromic fashion through the guidewire to the anterolateral position (Figure 3A and B). The LV lead pacing threshold was 0.8 V at 0.5 msec. The LV lead was subsequently tunnelled (Lead-extension Accessory kit, Medtronic) subcutaneously to reach the right pocket and was connected to the previously implanted generator. No complications occurred.
Snare technique: Selective cannulation of the posterior cardiac vein (black arrow). Guidewire advanced through the anterior collateral veins and anastomotic vein directly back to the PLSVC (white arrow). Snare system introduced through a second sheath via the LSV up to the PLSVC (black arrow). LSV: left subclavian vein; PLSVC: persistence of the left superior vena cava.
There are previous case reports of CS and LV tributaries cannulation via the right subclavian vein in patients with PLSVC. However, this patient had been subjected to a prior unsuccessful right-sided LV lead implantation procedure. The most common causes of failure are tumultuous flow in the CS ostium and impossibility to use balloon occlusion catheters in a giant CS.1
LV lead implantation through a left-sided approach in PLSVC is feasible but technically challenging. The use of a snare system to assist the placement of the LV lead was chosen due to the presence of small vessels (collaterals) in the posterolateral area with adequately sized vessels in the lateral area. The snare technique has been described in patients where delivery of the LV lead to the target vessel cannot be obtained with the standard approach. It is a safe technique and it reduces percutaneous implant failure and the subsequent need for a surgical approach.2,3 However, its use in patients with anatomical variants such as PLSVC had not been previously described.
The snare system is a useful new tool for LV lead implantation in patients with PLSVC and an adequate venous collateral anatomy.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.