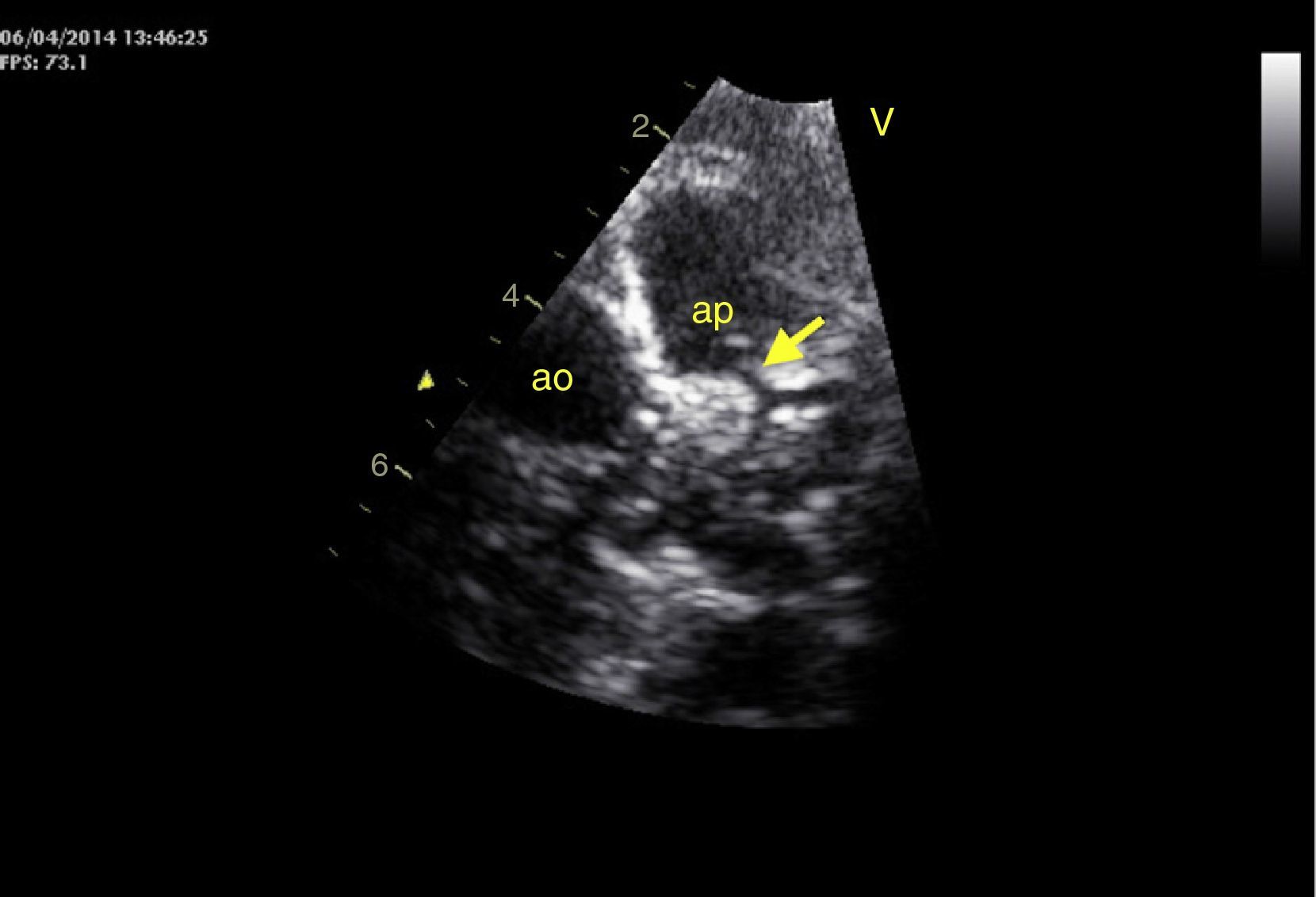
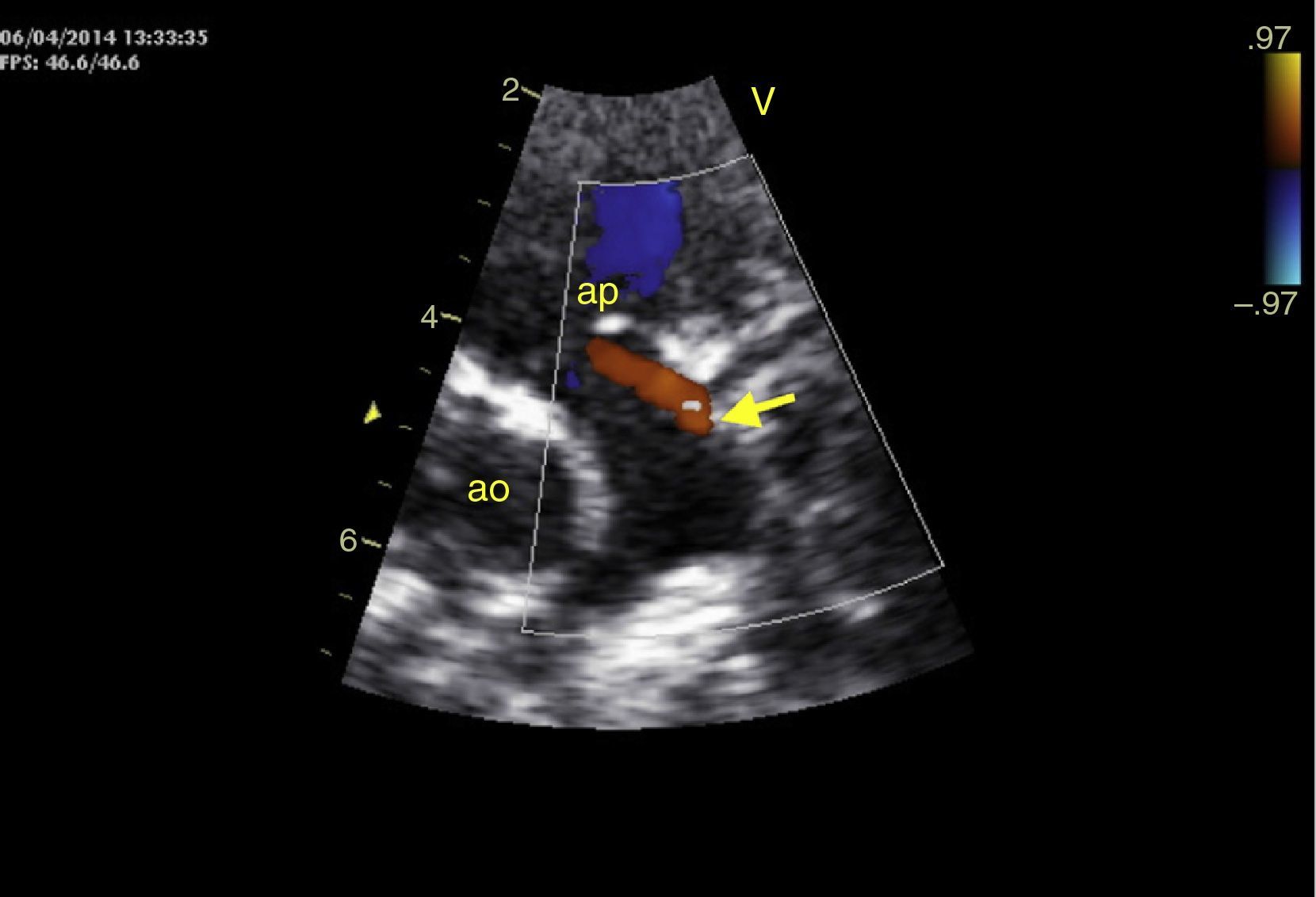
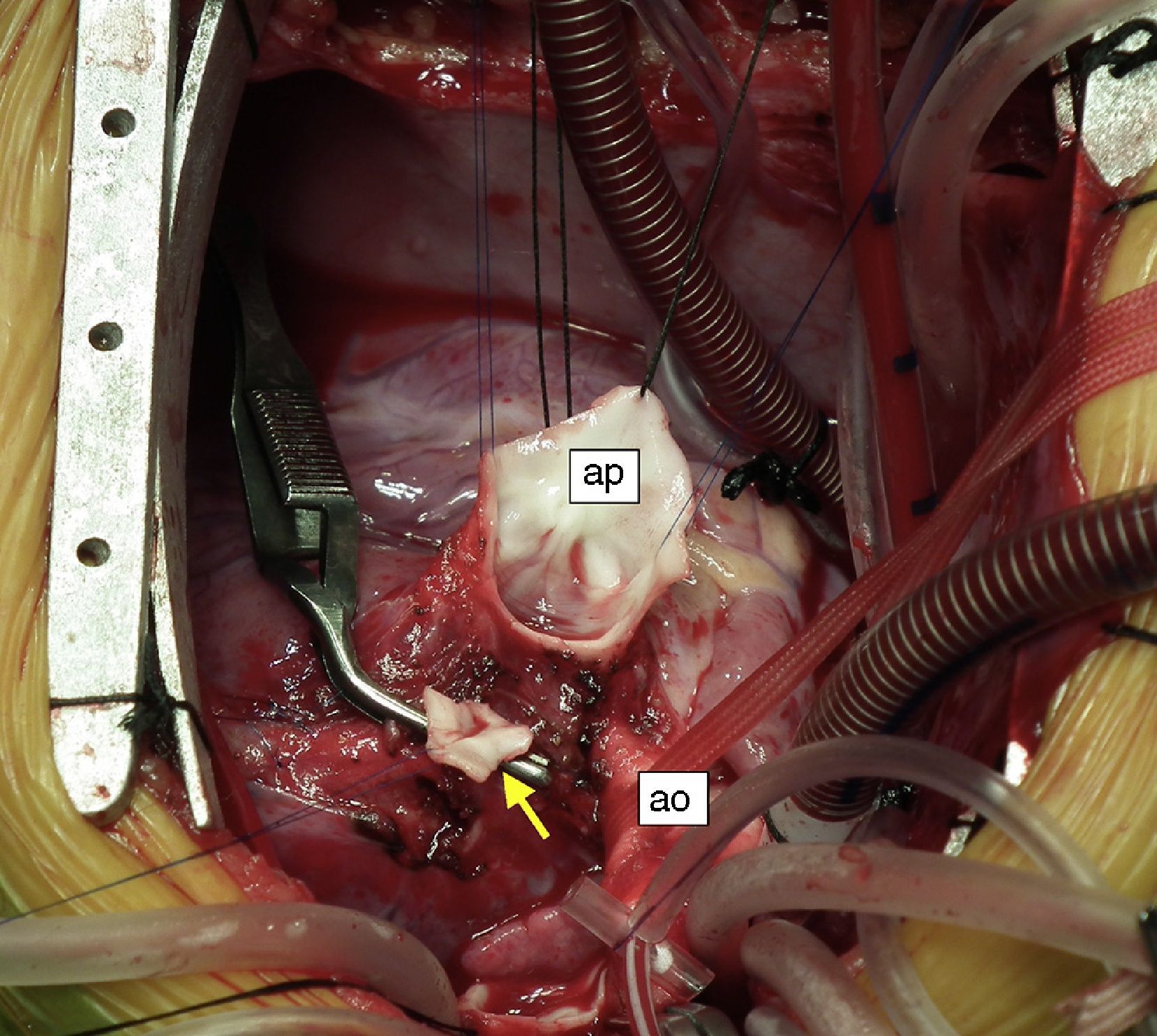
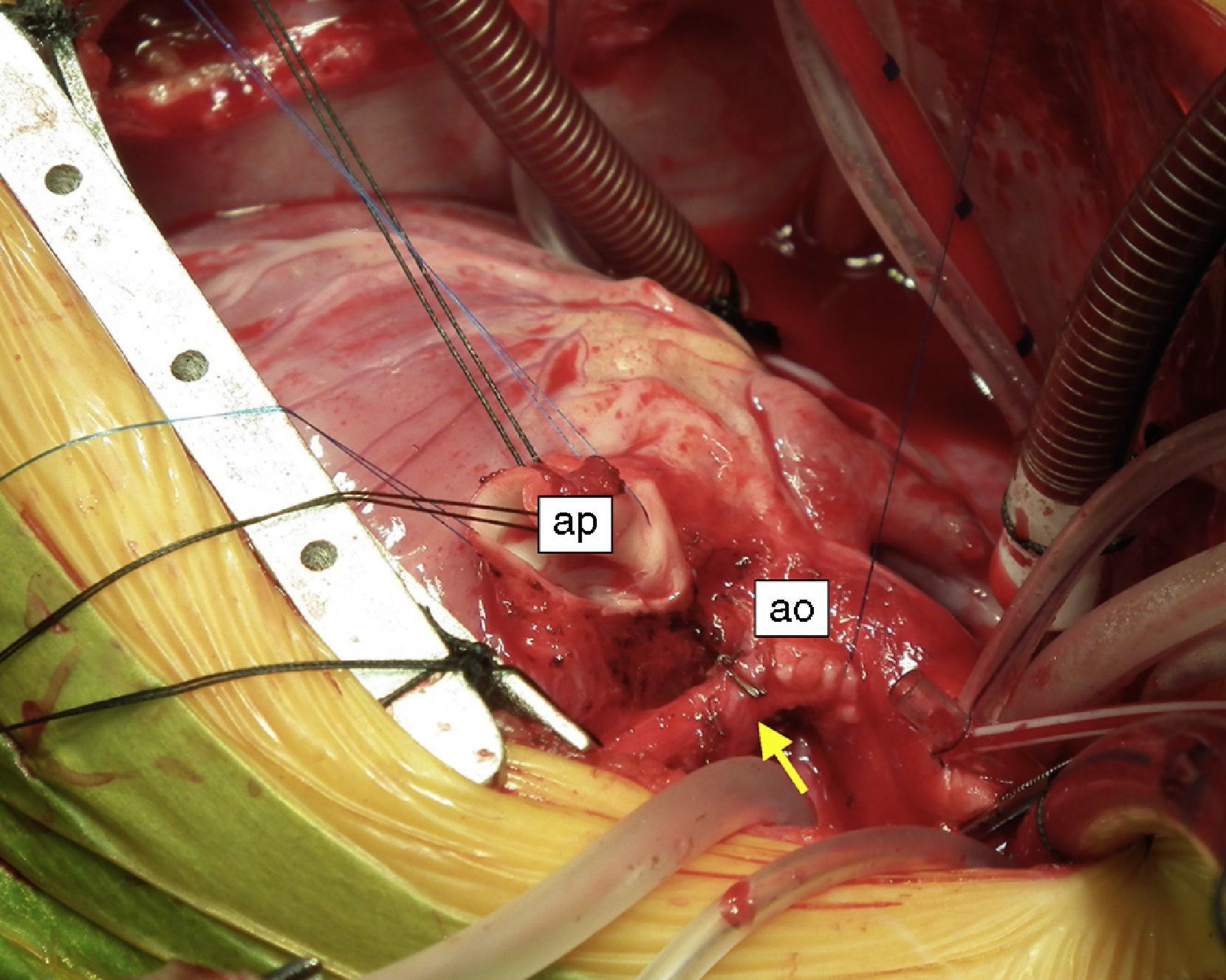
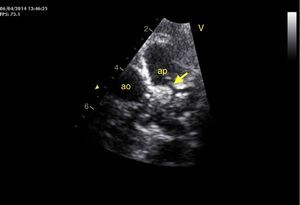
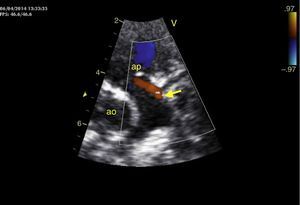
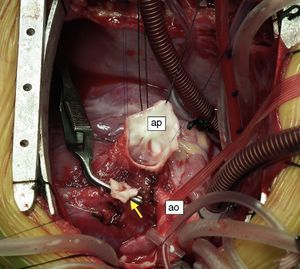
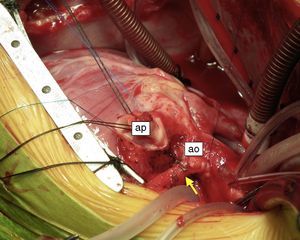
An eight-month old female infant had a history of poor weight gain from the age of four months and two bouts of pneumonia, at five and eight months. On physical examination she presented polypnea, S3 and a grade III/VI holosystolic murmur over the apex, radiating to the axilla. The chest X-ray revealed cardiomegaly, with a cardiothoracic index of 60%, and electrocardiography showed >3 mm Q waves in DI, aVL and V7 and T-wave inversion in V5-V7, suggestive of myocardial infarction. Transthoracic echocardiography revealed left ventricular (LV) dilatation and global dysfunction, with LV diastolic diameter (LVDD) 46 mm (Z-score +12.44), fractional shortening (FS) 16% and biplane ejection fraction (EF) 25.4%, severe mitral regurgitation with poor leaflet coaptation, and an anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (ALCAPA) (Figures 1 and 2). The patient was referred for surgery on the basis of the information obtained from these exams. Surgical correction consisted of reimplantation of the left coronary artery in the aorta (Figures 3 and 4). The surgery and postoperative period were uneventful. The patient was discharged eight days later, with reduced LV dimensions and significant improvement in global systolic function (LVDD 33 mm, Z-score +5.22, FS 23% and biplane EF 41.3%). Three months after the surgery, the child was clinically well with normal ventricular function.
Although rare, ALCAPA must be excluded as the cause of LV dilatation and dysfunction in newborns and infants, since it can be surgically corrected, with excellent prognosis at this age.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Please cite this article as: Araújo AR, Mendes IC, Magro P, Teixeira A, Neves JP, Anjos R. Disfunção ventricular grave mas reversível no lactente. Rev Port Cardiol. 2015;34:365–366.