We describe the case of a 62-year-old female patient with bilateral subclavian vein occlusion, in whom a cardiac resynchronization system was implanted via a femoral vein.
Os autores descrevem a implantação de sistema de ressincronização ventricular por via femoral, em doente do sexo feminino, 62 anos, com oclusão bilateral da veia subclávia.
We describe the case of a 62-year-old female patient in whom a cardiac resynchronization (CRT) system was implanted via a femoral vein. She had a history of Hodgkin's lymphoma in 2001, complicated by superior vena cava syndrome, had undergone chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and was in remission since then. In 2006 she underwent percutaneous coronary intervention with left main coronary artery stenting due to complaints of angina. In 2010, she developed left bundle branch block, and myocardial scintigraphy revealed left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 40%, without ischemia. In 2014 she developed symptoms of heart failure. An attempt was made to optimize medical therapy on an outpatient basis, but her clinical condition deteriorated and in February 2015 she was admitted to the hospital with severe heart failure (New York Heart Association [NYHA] functional class IV). The echocardiogram showed an LVEF of 25%, moderate to severe mitral regurgitation, preserved right ventricular systolic function and moderate pulmonary hypertension. Levosimendan perfusion was instituted and drug therapy was titrated (although hypotension precluded achievement of reasonable doses of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and beta-blockers), with progressive improvement to NYHA class III. Repeat coronary angiography showed no residual coronary disease and implantation of a CRT system was proposed. An attempt to implant a CRT defibrillator was unsuccessful due to bilateral subclavian vein occlusion. Surgical implantation of an epicardial left ventricular lead was not undertaken due to the patient's frailty and the strong possibility of severe mediastinal fibrosis, increasing the risk of procedural morbidity. We proposed implantation of a CRT system via a femoral approach, which was accepted by the patient. Considerations of generator size and weight, the low probability of obtaining an effective defibrillation vector at the level of the femoral region, and the fact that the patient was hospitalized for advanced heart failure, led to the selection of a pacemaker system.
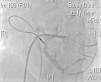
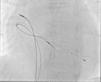
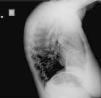
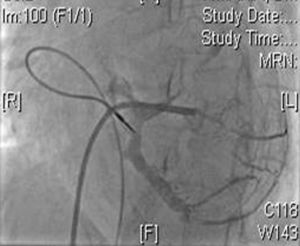
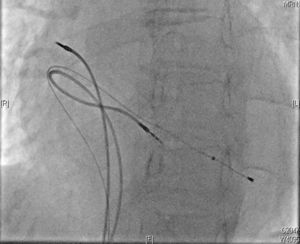
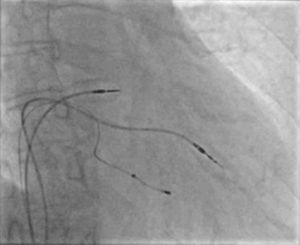
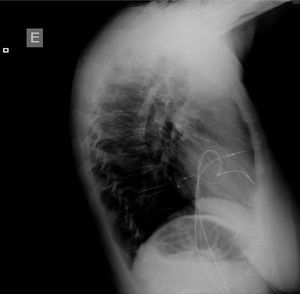
Two active fixation leads (85 cm Medtronic CapSureFix Novus® 5076) were implanted via the right femoral vein using peel-away introducers and positioned in the right ventricular septum and right atrial roof. Acute thresholds were 0.6 V for the right ventricle and 2.0 V for the right atrium, with impedances of 520 and 600 Ω, respectively. The R wave was measured at 5.5 mV and the P wave at 2.6 mV. A coronary sinus sheath (57 cm Medtronic Attain Command® with SureValve 6250VI-EHXL) was introduced over a deflectable electrophysiology catheter (Bard Dynamic XT) and advanced to the coronary sinus. Venography was performed (Figure 1) and a posterolateral vein was selected for placement of an 88 cm Medtronic Attain Ability® 4196 bipolar lead (Figures 2–4). These leads, as well as the coronary sinus sheaths, were selected because of their longer length, as the patient's height was 174 cm. A femoral pocket was created in the upper leg. The three leads and the generator were fixed to the muscle under the aponeurosis, using silk sutures.
Fluoroscopy time was 16 minutes and the entire procedure took less than two hours. Recovery was complicated by a pocket hematoma related to early administration of enoxaparin, which required surgical drainage. The patient was kept under permanent oral anticoagulation with warfarin.
The first follow-up visit took place 40 days after implantation. Her condition had improved markedly, and she presented in NYHA class II. The pacing system was working properly. Pacing thresholds were 0.75 V for the right atrium, 1.0 V for the right ventricle and 0.625 V for the coronary sinus lead. The measured P wave was 4.1 mV and the R wave in the right ventricular lead was 4.8 mV. Impedances were 418, 437 and 418 Ω in the right atrium, right ventricle and coronary sinus, respectively. At the last follow-up visit, nine months after implantation, the thresholds remained stable (thresholds, sensing and impedances were 0.75 V/3.9 mV/456 Ω for the right atrium and 0.75 V/3.8m V/475 Ω for the right ventricle; threshold and impedance for the coronary sinus lead were 0.75 V and 470 Ω), and she is still in NYHA class II, with no further hospital readmissions.
DiscussionAlthough there are only a few cases described in the literature,1–4 this report shows that implantation of a CRT system through a femoral approach is feasible and sometimes relatively easy, with good stability of the leads at nine-month follow-up. In patients with comorbidities and high surgical risk it can be a good alternative to the epicardial approach.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.