The Szabo technique provides a unique way to accurately position a stent in ostial lesions, avoiding geographic miss and shifting of plaque to non-affected adjacent vessels.
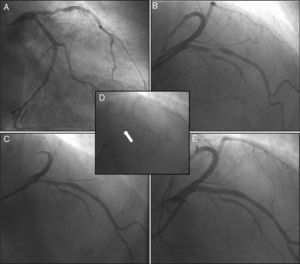
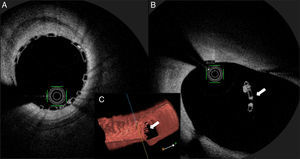
A 64-year-old woman with dyslipidemia presented to the emergency department with unstable angina. Coronary angiography showed single-vessel disease, with severe proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery stenosis and a critical bifurcation lesion of the mid LAD and the first major septal branch (Medina score 1,1,1) (Figure 1A and B). The left coronary ostium was cannulated with a 3.5F Extra Back-up® guide catheter, two BMW® wires were advanced to the LAD and the first septal branch, and the latter was treated with a 2.0 mm×15 mm drug-eluting balloon. After proximal and mid LAD predilation (Figure 1C), a 3.5 mm×28 mm Absorb GT1® bioresorbable scaffold (BRS) was advanced to the LAD, but deployment was not performed, due to device movement and unstable scaffold position (Video 1). An anchor wire crossed through the proximal BRS trailing strut was advanced to the circumflex (Figure 1D, arrow), and the BRS was implanted in the ostial LAD, with a good angiographic result (Figure 1E). Intracoronary optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed optimal strut apposition (Figure 2A) and the small anchoring strut floating in the circumflex ostium, as depicted by the arrow in Figure 2B (OCT view from the LAD) and Figure 2C (three-dimensional OCT reconstruction view from the LAD).
Coronary angiography showing severe disease of the mid left anterior descending (LAD) artery, involving the bifurcation with the first major septal branch (Medina 1,1,1) (A and B); after angioplasty of the first septal branch with a drug-eluting balloon and LAD predilation (C), a bioresorbable scaffold was implanted in the mid LAD using the Szabo technique (D and E).
To our knowledge, this case reports for the first time the feasibility and safety of the Szabo technique in an ostial lesion with BRS implantation. The use of intracoronary OCT imaging enabled us to ensure and document an excellent result with this technique.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.