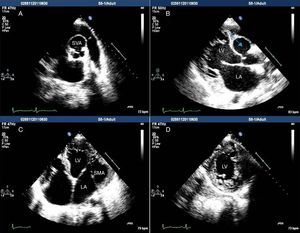
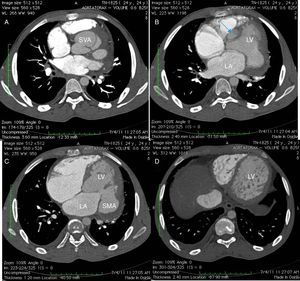
A 24-year-old black man presented to the emergency department of our hospital with fatigue and dyspnea at rest of two weeks duration. The transthoracic echocardiogram (Figure 1) revealed aneurysm of the right sinus of Valsalva (Figure 1A) dissecting into the interventricular septum (arrow) (Figure 1B), dilated left ventricle with moderately to severely impaired systolic function, and echocardiographic criteria for left ventricular non-compaction (Figure 1C and D). A submitral aneurysm and a dilated left atrium were also observed (Figure 1C). Doppler echocardiography showed mild mitral and aortic regurgitation. Multislice computed tomography with contrast (Figure 2) revealed an aneurysm of the right sinus of Valsalva (Figure 2A) dissecting into the interventricular septum (arrow) (Figure 2B), as well as a submitral aneurysm (Figure 2C) and non-compaction of the left ventricle (Figure 2D), confirming the echocardiographic findings. The patient was admitted to the cardiac intensive care unit of our hospital and treated with diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and digitalis, with dramatic improvement in symptoms. He was proposed for surgery but refused and was discharged in New York Heart Association class I. The patient died one year after the first admission.
Subvalvular aneurysms are relatively rare, and left ventricular non-compaction is a rare cause of cardiomyopathy. In an exhaustive literature review we found coexistence of both sinus of Valsalva and submitral aneurysms in only a few case reports since the first in 1962. The association of sinus of Valsalva aneurysm and left ventricular non-compaction is extremely rare, reported in only two cases. Furthermore, we found no published cases of the association of sinus of Valsalva aneurysm dissecting into the interventricular septum, submitral aneurysm and left ventricular non-compaction in the same patient. This case supports the theory that these aneurysms are congenital in etiology.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data and that all the patients included in the study received sufficient information and gave their written informed consent to participate in the study.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe author has no conflicts of interest to declare.