Intercoronary communication is a very rare coronary artery anomaly. It is defined as an open‐ended circulation with bidirectional blood flow between two coronary arteries. Coronary artery fistulas are abnormal communications between a coronary artery and a cardiac chamber or major vessel. A 62‐year‐old man was admitted to our hospital with sudden development of general weakness, dizziness and a sensation of compression in his chest. At presentation his blood pressure was 80/40 mmHg and heart rate was 65 beats/min. The ECG revealed sinus rhythm and 1–2 mm ST elevation in the anterior leads. The patient was taken to the catheterization laboratory for percutaneous coronary intervention. The left main and left circumflex coronary arteries were normal. Coronary angiography showed a communication between the left main and the diagonal branch of the left anterior descending and a fistula between the intercoronary connection and the left atrium. The other coronary arteries were normal. Laboratory test results, including cardiac troponin I and creatine kinase–MB levels, were normal. The angina symptoms disappeared and the ST elevation resolved within four hours. We report an interesting case of congenital coronary artery fistula in an intercoronary communication between the left main and the diagonal branch of the left anterior descending coronary artery presenting as an acute coronary syndrome. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case in the literature involving a coronary artery fistula in an intercoronary communication.
A comunicação intercoronária é uma anomalia muito rara da artéria coronária. Define‐se como circulação em aberto com um fluxo sanguíneo bidirecional entre as duas artérias coronárias. As fístulas das artérias coronárias são comunicações anormais entre a artéria coronária e uma câmara cardíaca ou um vaso principal. Um homem de 62 anos foi admitido no nosso hospital revelando fraqueza geral súbita, tonturas e sensação de compressão no peito. No momento apresentava pressão arterial de 80 mmHg/40 mmHg e frequência cardíaca de 65 batimentos/min. O eletrocardiograma (ECG) revelou ritmo sinusal e elevação do segmento ST de 1‐2 mm nas derivações anteriores. O doente foi conduzido para o laboratório de hemodinâmica para intervenção coronária percutânea. O tronco comum e as artérias coronárias circunflexas esquerdas estavam normais. A angiografia coronária mostrou uma comunicação entre o tronco comum e o ramo diagonal da artéria descendente anterior e uma fístula entre a comunicação intercoronária e a aurícula esquerda. As outras artérias coronárias estavam normais. Os resultados dos testes laboratóriais, incluindo os níveis de troponina I cardíaca e de creatina‐kinase MB estavam normais. Os sintomas de angina desapareceram e a elevação do segmento ST foi resolvida após 4 horas. Relatamos um caso interessante de uma fístula congénita da artéria coronária na comunicação intercoronária entre o tronco comum e o ramo diagonal da artéria coronária descendente anterior esquerda apresentadas como uma síndrome coronária aguda. De acordo com o nosso conhecimento relatamos o primeiro caso na literatura que envolve uma fístula da artéria coronária na comunicação intercoronária.
Intercoronary communication is a very rare coronary artery anomaly, with a prevalence of 2.37/100 000. It is defined as an open‐ended circulation with bidirectional blood flow between two coronary arteries.1 It can be distinguished from collateral arteries by its angiographic features, and in itself does not usually reflect underlying coronary artery disease.2 Intercoronary arterial connections are thought to be congenital in origin. Compared with collaterals, intercoronary arterial connections are larger in diameter (>1 mm), extramural, and straight. Furthermore, the structure of an intercoronary arterial connection is typical of an epicardial coronary artery, with a well‐defined muscular layer.3
Coronary artery fistulas are abnormal communications between a coronary artery and a cardiac chamber or major vessel.4 They may be congenital or acquired due to trauma or iatrogenic causes. Angiographic series reveal an incidence of coronary artery fistula in adults of 0.3–0.8%.4–6 Most of these patients are asymptomatic, but heart failure, angina, myocardial infarction, coronary steal, endocarditis, and dyspnea have been reported.7
We report an interesting case of congenital coronary artery fistula in an intercoronary communication between the left main and the diagonal branch of the left anterior descending coronary artery presenting as an acute coronary syndrome.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case in the literature involving a coronary artery fistula in an intercoronary communication.
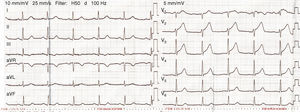
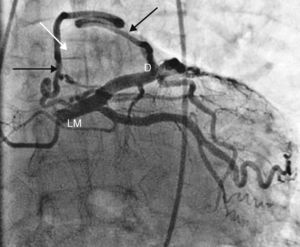
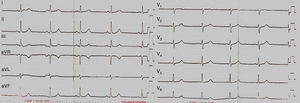
Case reportA 62‐year‐old man was admitted to our hospital with sudden development of general weakness, dizziness and a sensation of compression in his chest. He had a history of diabetes mellitus. At presentation his blood pressure was 80/40 mmHg and heart rate was 65 beats/min. The ECG revealed sinus rhythm and 1–2 mm ST elevation in the anterior leads (Figure 1). The patient was taken to the catheterization laboratory for percutaneous coronary intervention. The left main and left circumflex coronary arteries were normal. Coronary angiography showed a communication between the left main and the diagonal branch of the left anterior descending and a fistula between the intercoronary connection and the left atrium (Figure 2). The other coronary arteries were normal. Laboratory test results, including cardiac troponin I and creatine kinase–MB levels, were normal. The angina symptoms disappeared and the ST elevation resolved within four hours (Figure 3). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case in the literature involving a congenital coronary artery fistula in an intercoronary communication.
The hemodynamic consequences of coronary artery fistulas are variable depending on shunt size, site of the shunt and presence of other underlying heart disease.8 Fifty percent of patients with large or multiple fistulas may develop complications, which may include bacterial endocarditis, thrombosis, aneurysm formation, dissection, rupture, premature atherosclerosis, pulmonary hypertension, myocardial ischemia, or infarction.9
The functional significance of large intercoronary communications between normal coronary arteries is unclear but one may speculate that they have a potential role in protecting the myocardium should significant atherosclerosis develop in either of the patent arteries3; on the other hand, myocardial ischemia could result if an unidirectional intercoronary communication causes a coronary steal phenomenon that results in inadequate perfusion.10 The ischemic consequences of an intercoronary connection with unidirectional flow may be explained by its similarity to a fistula from a coronary artery to a low‐pressure cardiac space.11
We believe that an intercoronary communication between the left main and the diagonal branch of the left anterior descending coronary artery and a congenital coronary artery fistula may be the cause of ischemia in this case.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that the procedures followed were in accordance with the regulations of the relevant clinical research ethics committee and with those of the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki).
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data and that all the patients included in the study received sufficient information and gave their written informed consent to participate in the study.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the written informed consent of the patients or subjects mentioned in the article. The corresponding author is in possession of this document.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.