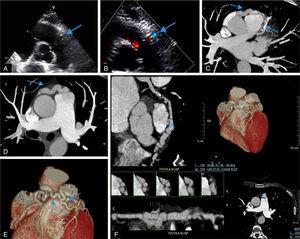
A 54-year-old asymptomatic woman presented to our echocardiography department for assessment of a continuous heart murmur. The transthoracic echocardiogram in parasternal short-axis view (Figure 1A) revealed a tunnel-like communication between the pulmonary artery trunk and the pericardial space (maximum width 8 mm). Color Doppler showed turbulent flow and pulsed wave Doppler showed typical continuous flow (Figure 1B). No valvular abnormalities were noted. There was a normal balance between the right and left ventricle, with preserved global systolic function. The estimated shunt by Qp/Qs was 1.3:1.0. The cardiac computed tomography scan revealed a large coronary artery fistula (CAF) between the left descending coronary artery and pulmonary artery trunk and also an aneurysmatic, tortuous CAF between the right coronary artery and pulmonary artery trunk (Figure 1C–F). A maximal exercise test was performed that excluded myocardial ischemia. She is currently asymptomatic and no cardiac events were noted in two-year follow-up.
(A and B) Transthoracic echocardiogram and color Doppler showing tunnel-like communication (arrows). (C and D) Cross-sectional computed tomography image showing the courses of the fistulae (arrows). (E and F) Three-dimensional volume-rendered multislice multiplanar reconstruction computed tomography views showing the courses of the fistulae (arrows and asterisk).
We present this case because bilateral coronary to pulmonary artery fistulae are a very rare entity. CAFs found to originate from both coronary arteries are rare and the pulmonary vasculature is the most uncommon site of termination.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that the procedures followed were in accordance with the regulations of the relevant clinical research ethics committee and with those of the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki).
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the written informed consent of the patients or subjects mentioned in the article. The corresponding author is in possession of this document.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.