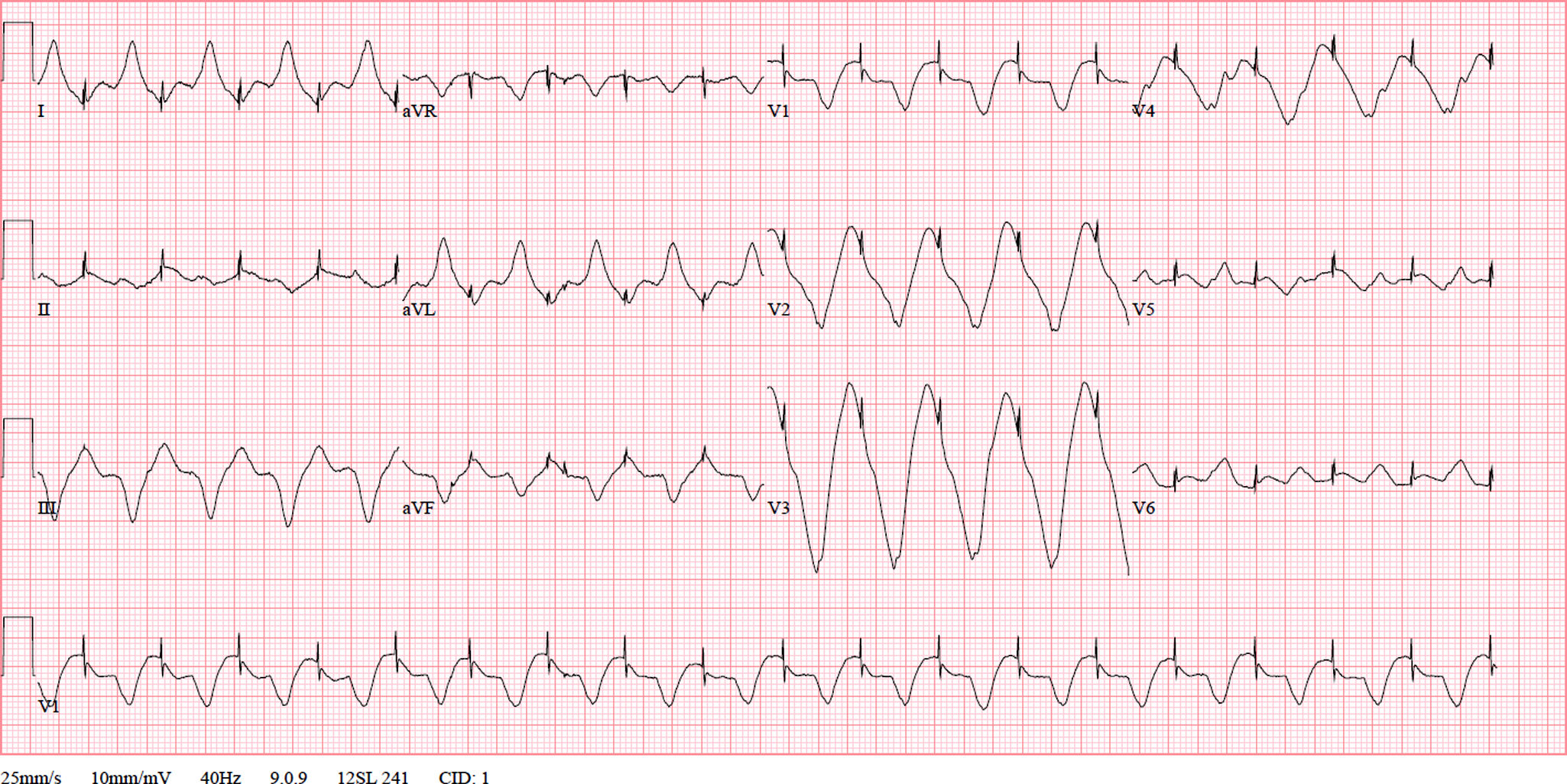
We present the case of an 81-year-old male with tachycardia–bradycardia syndrome, alternating between atrial fibrillation and persistent atypical atrial flutter. No structural heart disease was identified. The patient has a dual-chamber pacemaker in DDDR-ADIR mode and was being treated with flecainide 100 mg every 8 hours and atenolol 50 mg every 24 hours.
The patient presented to the emergency department with general malaise and profuse sweating lasting one day, without palpitations. The initial electrocardiogram (ECG) (Figure 1) showed a regular wide-QRS tachycardia at 145 bpm, leading to a diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia in the emergency department. A pacemaker evaluation revealed atrial tachyarrhythmia with pacemaker-mediated ventricular stimulation and a highly aberrant paced QRS. Due to suspected flecainide toxicity, the drug was discontinued, and treatment with bicarbonate was initiated.
Subsequent pacemaker interrogation revealed an episode of atrial flutter with a rate below the threshold for mode switching.
Flecainide is a Class IC antiarrhythmic drug according to the Vaughan Williams classification, widely used for the treatment of atrial tachyarrhythmias in the absence of structural heart disease. It primarily acts by blocking sodium channels, and its main electrocardiographic manifestation is the widening of the QRS complex, as observed in this case.1,2
Ethical approvalAn anonymized clinical case is presented. Informed consent was obtained from the patient.
FundingNo funding was received for the preparation of this scientific article.
Conflicts of interestThere are no conflicts of interest from any of the authors.