Sialadenitis is an extremely rare complication of procedures involving intravenous iodinated contrast medium. It was first described in 1956 by Sussman and Miller,1 who coined the term ‘iodide mumps.’ To date, fewer than 10 cases of sialadenitis associated with coronary angiograms (CAs) have been described in the literature.2 The mechanism behind iodide-induced sialadenitis is not well understood and may be either idiosyncratic or related to toxic accumulation of iodide in the salivary glands. Two percent of the dose is excreted via the salivary glands and can affect them bilaterally or unilaterally.3
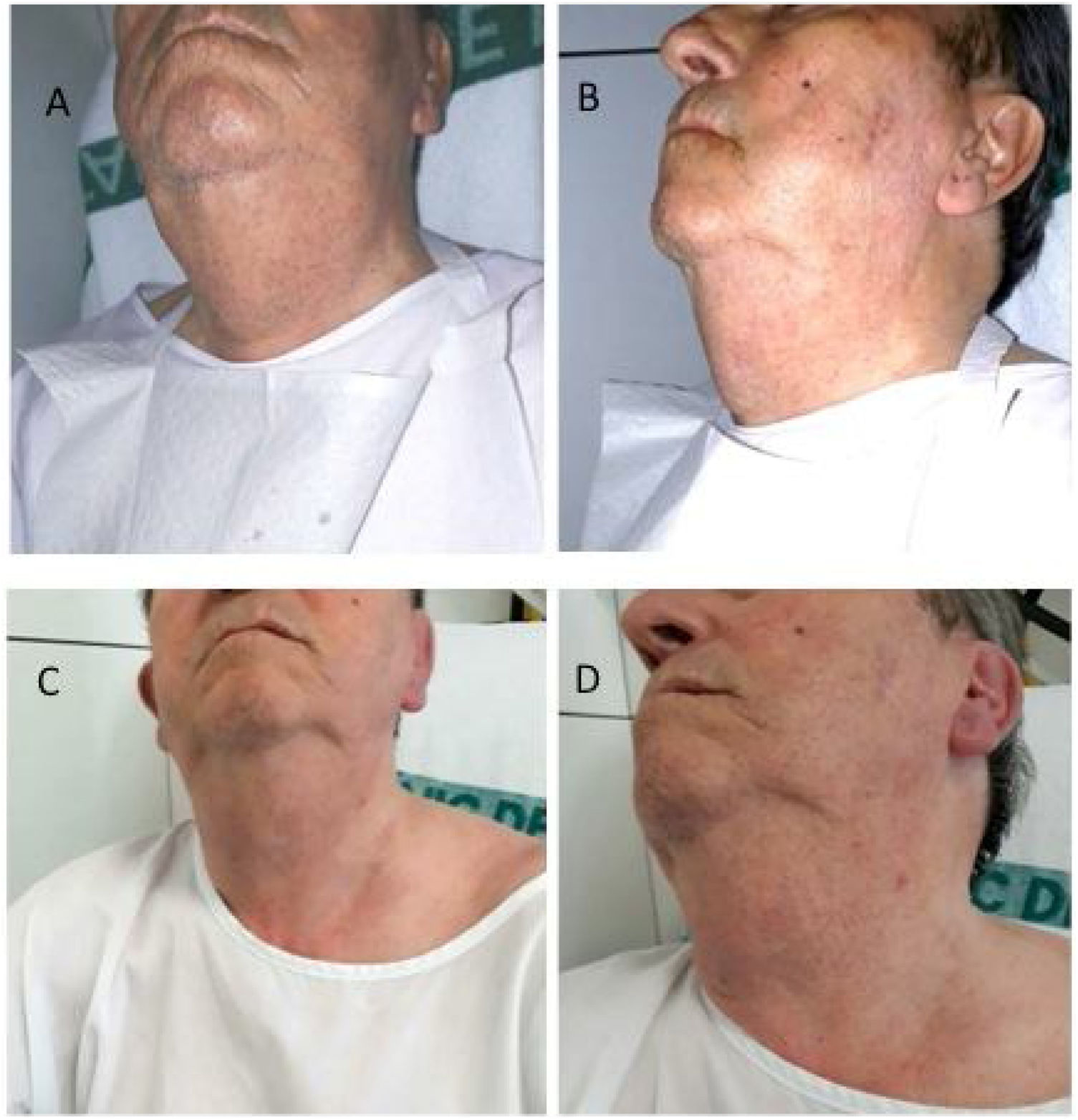
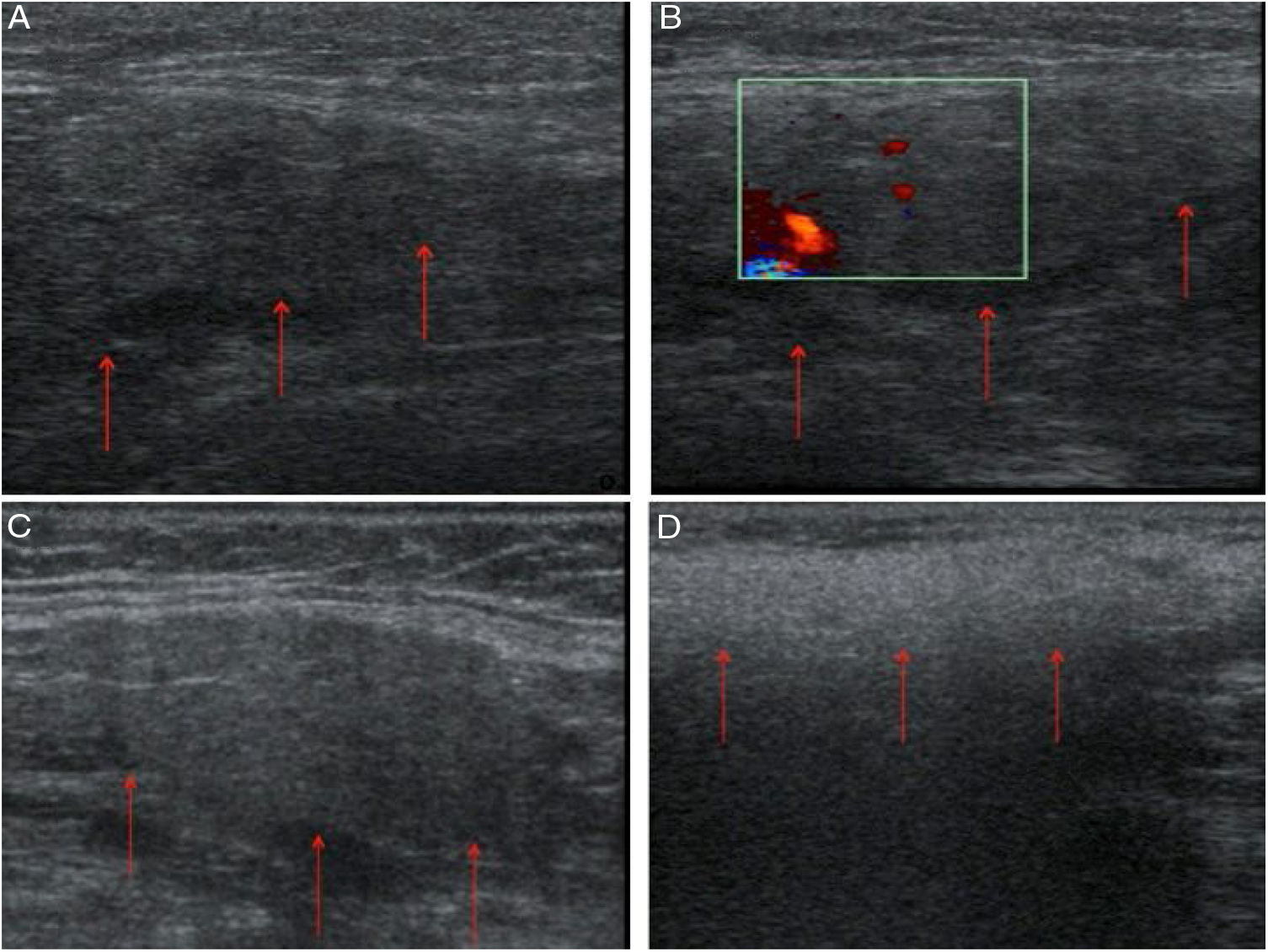
An 82-year-old man with no history of anaphylaxis and previous aortic valve replacement and a saphenous vein graft to the circumflex coronary artery was referred to our center for a scheduled outpatient CA to address progressive angina over recent months. Two previous CAs were performed without stenting, vascular, or anaphylactic complications. A drug-eluting stent was implanted in a severe lesion in the mid portion of the left descending coronary artery without immediate complications. Six hours post-procedure, the patient noticed bilateral neck swelling predominantly on the right side. Physical examination revealed enlargement and a slight tenderness of the right submandibular gland without airway compromise (Figure 1A and B). Intravenous antihistamine and corticoids were initiated. His medical chart revealed no current or recent use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers. A diagnosis of sialadenitis secondary to the use of iodinated contrast medium was assumed. Salivary gland ultrasound demonstrated homogenous inflammation of the right submandibular gland without dilated ducts and normal color velocity. These findings were compatible with non-infectious sialadenitis (Figure 2A-C).
The corticoids and antihistamine were stopped, and the patient's clinical picture and echocardiographic abnormalities resolved after three days (Figures 1B and C and 2D).
Iodide sialadenitis is a rare late reaction to intravascular administration of iodine-containing contrast material leading to abnormal swelling of the salivary glands. In our case, it occurred within six hours of exposure to iodine contrast media.3 The risk for sialadenitis appears to be directly related to serum iodide levels, identifying renal insufficiency and large iodide loads as predisposing factors. However, in our case, the patient's renal function was normal. Although the reaction often recurs with subsequent contrast administrations, our patient was exposed to iodide contrast in two previous CAs without incident. Treatment of this condition is largely supportive, and most cases resolve in two to four days without treatment.2,3
Given the widespread use of imaging and interventional techniques that use iodinated contrast, including CAs, physicians should be aware of this condition.
FundingNone.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.