Alcohol septal ablation (ASA) is an option in the treatment of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy refractory to medical therapy.1–3 Cardiac computed tomography (CT) is useful in the selection of patients, as it can simultaneously assess the coronary anatomy and its spatial relations with the myocardium, which is essential in determining the feasibility of ASA and selecting the appropriate septal artery. It can also evaluate the success of the procedure, by assessing the obstruction decreasing and the extent of fibrotic tissue (without additional contrast if performed immediately following ASA), at low dose radiation exposure.1–3
The authors present images illustrating the value of CT, comparing it with the other imaging modalities normally used in this context.
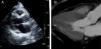
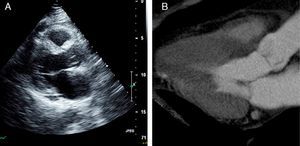
Figure 1 compares images of left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction by echocardiography (A) and CT (B), the latter also identifying a septal artery (arrow).
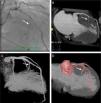
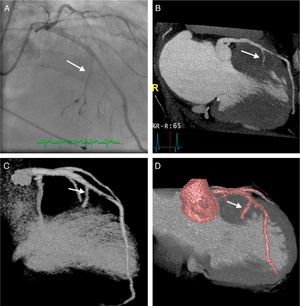
Figure 2 shows the anatomy of the septal arteries by invasive coronary angiography (A) and CT (B–D), showing the relationship between the septal arteries (arrow) and the ventricular chamber (C) and the hypertrophied myocardium (B and D).
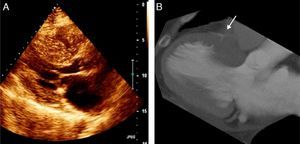
Images of the LVOT (Figure 3) by echocardiography (A) and CT (B) following ASA confirm the success of the procedure.
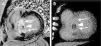
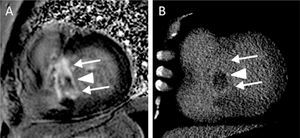
Figure 4 compares late enhancement images by magnetic resonance imaging (A) and CT (B) following ASA, showing areas of myocardial fibrosis (arrows) and microvascular lesion induced by alcohol ablation (triangle).
Cardiac CT is a non-invasive technique that can be used to plan ASA, assess the outcome and predict its long-term success.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data and that all the patients included in the study received sufficient information and gave their written informed consent to participate in the study.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Please cite this article as: Faustino, A; Utilidade da tomografia computorizada cardíaca no planeamento e avaliação do resultado da ablação septal por álcool. Rev Port Cardiol 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.repc.2012.07.009