Hypertension is an extremely prevalent disease worldwide and hypertension control rates remain low. Lack of adherence contributes to poor control and to cardiovascular events. No questionnaire in Portuguese is readily available for the assessment of adherence to antihypertensive drugs. We aimed to perform a translation and cultural adaptation to Portuguese of the Hill-Bone Compliance to High Blood Pressure Therapy Scale, a validated instrument to measure adherence in hypertensive patients.
MethodsA formal process was employed, consisting of a forward translation by two independent translators and a back translation by a third translator. Discrepancies were resolved after each step. Hypertensive patients were involved to identify and resolve phrasing and wording difficulties and misunderstandings.
ResultsThe forward and back translation did not produce significant discrepancies. However, important issues were identified when the questionnaire was presented to patients, which led to changes in the wording of the questions and in the format of the questionnaire.
ConclusionQuestionnaires are important instruments to assess adherence to therapy, particularly in hypertension. A formal translation and cultural adaptation process ensures that the new version maintains the same concepts as the original. After translation, several changes were necessary to ensure that the questionnaire was understandable by elderly, low literacy patients, such as the majority of hypertensive patients. We propose a Portuguese version of the Hill-Bone Compliance Scale, which will require validation in further studies.
A hipertensão arterial (HTA) é extremamente prevalente em todo o mundo e a proporção de doentes controlados permanece baixa. A má adesão à terapêutica dificulta o controlo da doença e contribui para a ocorrência de eventos cardiovasculares. Não existe nenhum questionário em português imediatamente disponível para avaliar a adesão a fármacos anti-hipertensores. O nosso objetivo é realizar a tradução e adaptação cultural do questionário de adesão Hill-Bone, um instrumento validado em doentes com HTA.
MétodosFoi utilizado um processo formal, consistindo numa tradução para português por dois tradutores, seguida de uma retroversão para inglês por um terceiro tradutor. As discrepâncias foram discutidas e resolvidas após cada passo. Doentes com HTA foram envolvidos, de forma a identificar e corrigir construções de frases e escolhas de palavras que provocaram problemas de compreensão.
ResultadosA tradução e retroversão não produziram discrepâncias relevantes. Foram identificados problemas de compreensão importantes quando o questionário foi apresentado aos doentes, motivando alterações na elaboração das perguntas e no formato do questionário.
ConclusãoOs questionários são instrumentos importantes na avaliação da adesão à terapêutica, em particular na HTA. O processo formal de tradução e adaptação cultural visa garantir que a nova versão mantém os mesmos conceitos que o original. Várias alterações foram necessárias para garantir que o questionário é corretamente interpretado por indivíduos idosos e com baixa literacia, características de grande parte dos doentes hipertensos. Propomos a versão portuguesa do questionário Hill-Bone de adesão à terapêutica anti-hipertensora, que deverá ser validada em estudos futuros.
Hypertension is a highly prevalent disease worldwide and is estimated to affect around 42% of Portuguese adults,1 a prevalence that is predicted to grow in the future.2 Over the last decade, considerable improvements have been achieved in the care of hypertensive patients in Portugal, with the proportion of those receiving treatment increasing from less than 40%3 to almost 75%; however, the proportion of controlled patients remains at an unsatisfactory 42.5%.1
Poor adherence to therapy is an issue in all chronic diseases and even more important in a largely asymptomatic disease like hypertension.4 It leads to lack of control5 and to a higher risk of cardiovascular events.6
Several methods exist to assess adherence, which can be divided into direct and indirect approaches.7 Direct methods, such as directly observed therapy or measurement of drug metabolites in plasma or urine samples, are cumbersome or technically complex,8,9 and are thus unavailable in daily practice. Indirect methods include electronic medication monitors, which are expensive and also largely unavailable outside the research environment,10 and questionnaires.
Adherence questionnaires have been developed, validated and used in patients with several chronic diseases.11,12 In hypertension, the most widely used questionnaire is the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale13 but its Portuguese version is not free to use without a license from the author. Another commonly used questionnaire is the Hill-Bone Compliance to High Blood Pressure Therapy Scale, which has been developed and validated in a low literacy setting, and its psychometric characteristics described.14 A Portuguese version of this questionnaire does not exist.
Given the need to assess adherence to therapy with a simple and readily available instrument in daily practice, it was our aim to perform a translation and cultural adaptation of the Hill-Bone Compliance Scale from the original English to Portuguese.
MethodsA formal translation and cultural adaptation process was performed, as recommended in the Principles of Good Practice of the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research regarding patient-reported outcomes (PRO) measures.15
As preparation, the authors of the original scale were contacted and provided authorization for the process; moreover, a member (CDH) of the team that developed and tested the original instrument was involved in the preparation of this manuscript. A working group was assembled, including physicians with experience in the care of hypertensive patients and physicians who have been responsible for the production, as well as translation and cultural adaptation, of questionnaires.16–18 Forward translation from English to European Portuguese was performed by two independent native Portuguese speakers who are fluent in English. Discrepancies were then discussed and resolved by consensus, involving the whole study group, producing a final forward translation version. Back translation was then performed by someone fluent in both languages who was neither involved in the previous steps nor familiar with the original scale. A more conceptual, rather than literal, style was employed in this step. The working group then compared the back translation against the original questionnaire in order to identify discrepancies in the concepts; if significant discrepancies were identified, the process of forward translation would be restarted.
Once no conceptual discrepancies were found between the original questionnaire and the Portuguese version, it was then presented to Portuguese-speaking hypertensive patients. Patients were recruited in the hypertension clinic of a University Hospital in Porto, Portugal. An effort was made to include patients with a variety of educational and cultural backgrounds. They were asked to fill the questionnaire paying particular attention to the construction and phrasing of the sentences, insuring that the concepts were interpreted appropriately. All patients’ difficulties or misunderstandings, as well as their opinions on the questionnaire, were analyzed and used as a basis for changes in the wording. This process was repeated until the questionnaire was understood correctly by the patients. The final version was reviewed by the working group and this report was prepared.
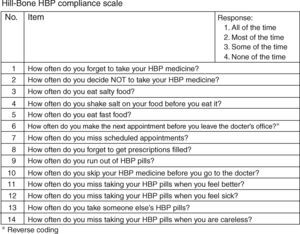
ResultsThe original version of the Hill-Bone Compliance Scale was obtained from the original authors (Figure 1), as well as authorization to perform the translation process. Several discrepancies occurred, namely in the translation of the expression “shake salt on your food” in question 4, and the verbs “skip” and “miss taking” from questions 10 and 12–14. All differences were discussed and resolved, and a final forward translation version was produced by consensus (Supplement 1). The back translation was performed and, despite some wording differences, the resulting version showed no conceptual discrepancies with the original scale.
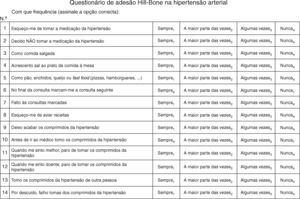
The Portuguese version was then presented to nine patients from the hypertension clinic. Numerous problems were identified, such as the expression ‘fast food’, which had been kept from the original and was not understood by most of the patients. The most important source of misunderstanding was the phrasing of questions 10, 11, 12 and 14 – patients tended to answer ‘All of the time’ (because they always took their medication) but the correct answer for that idea was ‘None of the time’. The translation into Portuguese of these questions implies a negative phrase and the desired answer ‘None of the time’ creates a double negative which was difficult for the patients. In addition, most patients had difficulties marking questions with a number that corresponds to a response option. In view of these findings, questions 10, 11 and 12 were changed to a positive phrasing, so that good adherence will produce a positive answer. Consequently, the score attributed to the response options for question 10 had to be changed, in order to preserve comparability with the scoring of the original scale. Furthermore, we changed the format of the questionnaire so that the response options are presented after the question (rather than a space to mark a number). This new version was presented to six other patients from the hypertension clinic. With the new version, no crucial difficulties or misunderstandings were detected. One patient had difficulty with question 2 (which also has a negative phrasing); we decided to maintain this phrasing and the capital letters for the negative particle, as in the original scale. Question 5 addresses the intake of food rich in salt; the available evidence shows that, in Portugal, most salt intake comes from salt-rich food, such as bread, cheese and sausages/cold meat.19 We therefore changed question 5 in order to include these examples. The final Portuguese version of the questionnaire (Figure 2) was reviewed and accepted by the working group.
DiscussionWe propose a Portuguese version of the Hill-Bone Compliance Scale, resulting from a formal translation and cultural adaptation process.
The development of PRO measures is crucial for the assessment of chronic diseases such as hypertension. Poor adherence to therapy is a major issue in hypertension care, but instruments that assess it are scarce. Despite multiple limitations, questionnaires are the most accessible instruments to assess adherence in daily clinical practice. PRO measures must be developed or translated to the language of the population that will use them. To our knowledge, no original European Portuguese adherence questionnaire or European Portuguese translations have been described in the literature.
The forward-backward translation process that we used is the most widely accepted method.15 Similar methods have been used for the translation of this questionnaire into other languages.20,21
Several difficulties were identified after the first version was presented to patients. It was clear that the phrasing obtained by translation from the original English was too complex in the Portuguese language, especially for a questionnaire that is meant to be used by an elderly population with low literacy. The changes were clearly necessary for cultural adaptation.
The main strength of this study is the use of a formal methodology, which ensures that the version obtained maintains the same concepts as the original scale. Other concepts or domains that might be useful in the evaluation of adherence could not be included when following the standardized international recommendations for a translation and cultural adaptation process.15 The use of other questionnaires that analyze different dimensions may provide a broader assessment of adherence, namely of the reasons for non-adherence. A minor limitation is the fact that the study was conducted in a hospital clinic, while the questionnaire is intended also to be used in a primary care setting. However, the patients involved were of similar age, literacy level and socioeconomic background to most hypertensive patients in primary care, had mostly essential, not resistant, hypertension, and were originally referred to the hospital by primary care physicians. Furthermore, we do not describe a validation process, and the psychometric characteristics of the Portuguese Hill-Bone Compliance Scale should be evaluated in the future.
ConclusionWe describe the translation and cultural adaptation of the Hill-Bone Compliance Scale and propose a European Portuguese version to be used with hypertensive patients in a primary or hospital setting. Further studies are necessary for the validation of this new version.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this investigation.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
We wish to thank Francisco Cunha, MD, Catarina Pereira, MD, Inês Costa, MD, Emanuel Araújo, MD, and Pedro Marques, MD for their assistance in the recruitment of patients to assess the Portuguese version of the questionnaire, as well as Sofia Silva, PhD, who conducted the back translation.