In recent years, various specific techniques and materials have been developed for the treatment of coronary chronic total occlusions (CTO).
ObjectiveTo evaluate the current situation in the treatment of CTO (techniques and material) in our setting.
MethodsWe evaluated data on techniques and material used in the CIBELES (ChronIc coronary occlusion treated By EveroLimus Eluting Stent) trial, a randomized comparison of sirolimus- and everolimus-eluting stents in 207 patients with CTO in 13 centers in Spain and Portugal.
ResultsA radial approach was used in 23% of patients, and retrograde techniques were used in only 5%. A high number of balloons were used (2.2±0.9 per patient). Microcatheters were used in 33% of patients, and post-dilatation balloons in only 25%. The mean number of stents implanted per patient was 2.1±1.0, with a mean total stent length of 49±24 mm. Other devices and techniques used were: Tornus penetration catheter in 4% of patients, rotational atherectomy in 2%, and cutting balloon in 1%. Intracoronary ultrasound was used in only 6% of patients. In 34% of cases, operators used guidewires that were not specifically for CTO. Considerable variability between centers was detected in the use of different techniques, the highest and lowest variability being observed in the use of intracoronary ultrasound and the use of CTO guidewires, respectively.
ConclusionsIn the CIBELES trial, techniques and devices specifically designed for the treatment of CTO were used in a relatively low proportion of patients. Considerable variability between centers was detected.
Durante os últimos anos foram desenvolvidos materiais e técnicas específicos para o tratamento de oclusões totais crónicas (OTC).
ObjetivoAvaliar a situação atual no tratamento de OTC (técnicas e material) na nossa realidade.
MétodosAvaliámos os dados relacionados com as técnicas e material usados no estudo CIBELES (ChronIc coronary occlusion treated By EveroLimus Eluting Stent) que comparou de forma aleatororizada stents eluidores de sirolimus e everolimus em 207 doentes com OTC em 13 centros de Espanha e Portugal.
ResultadosA abordagem radial foi usada em 23% dos doentes e as técnicas retrógradas foram usadas em apenas 5%. Foi usado um elevado número de balões (2,2±0,9 por doente). Microcatéteres foram usados em 33% e balões de pós-dilatação apenas em 25% dos doentes. O número médio de stents implantados por doente foi de 2,1±1,0, com um comprimento total médio de 49±24 mm. Outro material foi: tornus 4%, aterectomia rotacional 2% e cutting balloon em 1% dos doentes. Ecografia intra-coronária foi usada em apenas 6% dos doentes. Em 34% dos casos os operadores usaram fios-guia que não eram específicos de OTC. Uma alta variabilidade entre centros foi detetada no uso de diferentes técnicas, sendo a variabilidade observada mais alta e mais baixa no uso de ecografia intra-coronária e no uso de guias de OTC, respetivamente.
ConclusõesNo estudo CIBELES, técnicas e material especificamente desenvolvidos para o tratamento de OTC foram usados numa proporção relativamente baixa dos doentes. Foi detetada uma alta variabilidade entre centros.
Coronary chronic total occlusions (CTO) still constitute one of the most difficult challenges for interventional cardiologists, due mainly to difficulty in achieving adequate vessel recanalization, but also to high rates of restenosis, reocclusion, and new revascularization procedures in cases with an initial successful result.1–3 For these reasons, in recent years various specific devices and techniques have been developed and guidelines have been established for appropriate treatment of these lesions.4–6
Our objective was to assess the current situation regarding treatment of CTO in terms of devices and techniques used, based on the results of the CIBELES (ChronIc coronary occlusion treated By EveroLimus Eluting Stent) trial, a randomized comparison of sirolimus- and everolimus-eluting coronary stents in 207 patients with CTO.7,8
MethodsStudy populationThe CIBELES trial (Clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT00793221) included 207 patients with a coronary CTO with an estimated duration of occlusion >2 weeks.7,8 The patients were randomly allocated to everolimus-eluting (Xience V, Abbott Vascular) or sirolimus-eluting (Cypher, Cordis, Johnson & Johnson) coronary stents. In the latest guidelines on the treatment of CTO, CTO was defined as a total occlusion with an estimated duration of occlusion >3 months. However, in the CIBELES study an estimated duration of occlusion >2 weeks was used, for two reasons. First, most studies comparing different strategies to reduce restenosis in CTO included patients with an estimated duration of occlusion >2 weeks. Second, in the CIBELES study, two different types of drug-eluting stents were compared, taking late loss as the primary endpoint, and duration of occlusion has more impact on the probability of crossing the occlusion than on the risk of restenosis. Despite these two considerations, estimated duration of occlusion in the CIBELES study was >3 months in 80% of cases.8 Other inclusion and exclusion criteria have been previously published.7
Thirteen centers in Spain and Portugal participated in the study, all of them with a high volume of percutaneous coronary interventions on CTO. The Spanish Society of Cardiology sponsored the study, which was partly funded by an unrestricted grant from Abbott Vascular. The study was monitored by Chiltern International, and had an independent clinical events committee.
Data collectionFor every patient, data were collected on approach (anterograde or retrograde, femoral or radial), material and techniques used (types of guidewires, balloons, microcatheters, intravascular ultrasound, rotational atherectomy, etc.), type of anticoagulation and amount of contrast. All these aspects were left to the operators’ discretion, respecting local practice, and hence the data obtained reflect standard practice in each center.7
Statistical analysisThe statistical analysis was performed with SPSS version 12.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Continuous variables are presented as mean±standard deviation, and qualitative variables as proportions (percentages). Means were compared with the Student's t test, and proportions were compared using the chi-square test (with Fisher's correction when necessary). Differences were considered statistically significant with a p value <0.05.
In order to evaluate variability between different participating centers, the variation coefficient was calculated for different study variables (standard deviation/mean).
ResultsBaseline characteristics of the study population (Tables 1 and 2)The patients’ mean age was 64±10 years, and 83% were male. About 36% of patients were diabetic. Due to the inclusion criteria, all treated lesions were de novo and located in native vessels. The treated vessel was the left anterior descending artery, right coronary artery, and left circumflex artery in 41%, 39%, and 19%, respectively.
Baseline characteristics of the study population.
| Age (years) | 64±10 |
| Female gender (%) | 16.9 |
| Diabetes (%) | 36.2 |
| Treatment with insulin (%) | 7.7 |
| Hypertension (%) | 68.1 |
| Hypercholesterolemia (%) | 71.5 |
| Smoking (%) | 55.6 |
| Number of coronary risk factors | 2.3±1.0 |
| Previous percutaneous intervention (%) | 33.8 |
| Previous coronary bypass (%) | 4.3 |
| Previous myocardial infarction (%) | 37.7 |
| Duration of occlusion >3 months (%) | 79.7 |
| Peripheral arterial disease (%) | 11.6 |
| Clinical indication (%) | |
| Angina | 69.6 |
| Persistent ischemia | 30.4 |
| Non-invasive test (%) | 59.4 |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction (%) | 53±13 |
| Plasma creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.0±0.4 |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dl) | 120±50 |
| Number of diseased vessels | 1.8±0.8 |
| Multi-vessel disease (%) | 56.0 |
Angiographic characteristics of the study population.
| Treated vessel (%) | |
| Left main | 0.5 |
| Anterior descending | 41.1 |
| Left circumflex | 18.8 |
| Right coronary | 39.1 |
| Two vessels (right and circumflex) | 0.5 |
| Moderate or severe tortuosity (%) | 13.5 |
| Moderate or severe calcification (%) | 38.2 |
| Bifurcation (%) | 24.6 |
| Mean reference vessel diameter (mm) | 3.0±0.6 |
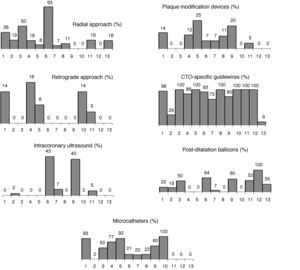
A radial approach was used in 23% of cases; a retrograde approach was used in only 5% of patients. The use of radial (0%-92%) and retrograde approaches (0%-18%) both showed considerable variability between participating centers (Figure 1).
Material, devices, and techniques used.
| Approach (%) | |
| Femoral | 76.8 |
| Radial | 23.2 |
| Size of guiding catheter (%) | |
| 6 French | 75.8 |
| 7 French | 11.6 |
| 8 French | 12.6 |
| Retrograde approach (n/%) | 4.8 |
| Number of guidewires | 2.0±1.2 |
| Number of microcatheters | 0.4±0.5 |
| Number of balloons | 2.2±0.9 |
| Pre-dilatation | 1.9±0.7 |
| Post-dilatation | 0.3±0.4 |
| Number of stents | 2.1±1.0 |
| Total stent length (mm) | 49±24 |
| Maximum stent diameter (mm) | 2.9±0.4 |
| Minimum stent diameter (mm) | 2.6±0.4 |
| Intracoronary ultrasound (%) | 5.8 |
| Other techniques (%) | 6.8 |
| Rotational atherectomy | 2.4 |
| Cutting balloon | 1.0 |
| Tornus catheter | 4.4 |
| Amount of contrast dye (ml) | 284±130 |
| Antithrombotic treatment (%) | |
| Unfractionated heparin | 86.5 |
| Bivalirudin | 12.1 |
| Enoxaparin | 1.4 |
| Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa blockers | 3.9 |
The mean number of guidewires used was 2.0±1.2. Asahi guidewires were the most frequently used (34.6%), followed by Abbott (21.2%) and Terumo (10.6%) guidewires. In 33.8% of cases, guidewires specifically designed for CTO were not used.
A large number of balloons (2.2±0.9 per patient) were used. Of these balloons, most were pre-dilatation balloons (1.9±0.7 per patient). Post-dilatation balloons were used in only 25% of patients, the number used per patient being 0.3±0.4. Microcatheters were used in 33% of patients (74 in 68 patients), the most frequent type being Finecross (Terumo) (77%), followed by Corsair (Asahi) (16%). Due to the study design, all patients received drug-eluting stents. The mean number of stents implanted per patient was 2.1±1.0, with a mean stent length of 49±24 mm.
Other devices and techniques used were Tornus penetration catheters (Abbott Vascular) in 4% of patients, rotational atherectomy (Boston Scientific) in 2%, and cutting balloon (Boston Scientific) in 1%. Importantly, intracoronary ultrasound during the procedure or after stent implantation was used in only 6% of procedures, also with considerable variability between participating centers (Figure 1).
Antithrombotic treatmentAntiplatelet therapy consisted of aspirin and clopidogrel in all patients. Additionally, 4% of patients received glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors. Anticoagulation during the procedure was performed with unfractionated heparin in most cases (87%), followed by bivalirudin (12%) and enoxaparin (1%). In eight of the 13 centers (62%), unfractionated heparin was the only anticoagulation used.
Variability between participating centersFigure 1 shows the variability between participating centers. The greatest variability was observed in the use of intracoronary ultrasound (variation coefficient 2.14), and the least was found in the use of guidewires specific for CTO (variation coefficient 0.37).
Comparison between patients with a duration of occlusion >3 months vs. <3 monthsTable 4 shows the comparison between patients with an estimated duration of occlusion >3 months and <3 months. Of the 207 patients, 165 (80%) had an estimated duration of occlusion >3 months. These patients had higher rates of specific techniques for CTO (specific guidewires, microcatheters, etc.), but the differences were statistically significant only in the use of a radial approach (20% vs. 36%; p=0.031). A retrograde approach was used in 6% of patients with duration of occlusion >3 months, compared to 0% in patients with estimated duration of occlusion of between 2 weeks and 3 months. A trend for a higher rate of use of plaque modification devices (rotational atherectomy, cutting balloon, Tornus catheter) was found in patients with >3 months since occlusion (9% vs. 0%, p=0.078).
Comparison between patients with estimated duration of occlusion >3 months and <3 months.
| <3 months | >3 months | p | |
| n | 42 | 165 | |
| Approach (%) | 0.031 | ||
| Femoral | 64.3 | 80.0 | |
| Radial | 35.7 | 20.0 | |
| Size of guiding catheter (%) | 0.071 | ||
| 6 French | 88.1 | 72.7 | 0.043 |
| 7 French | 9.5 | 13.3 | |
| 8 French | 2.4 | 13.9 | |
| Retrograde approach (n/%) | 0.0 | 6.1 | 0.218 |
| Number of guidewires | 1.6±0.8 | 2.1±1.2 | 0.135 |
| Use of specific guidewires (%) | 57.1 | 68.5 | 0.165 |
| Use of microcatheters (%) | 28.6 | 34.5 | 0.463 |
| Number of balloons | 1.8±0.7 | 2.0±0.7 | 0.133 |
| Number of stents | 1.9±0.9 | 2.1±1.0 | 0.192 |
| Total stent length (mm) | 45.2±22.4 | 49.7±24.5 | 0.299 |
| Maximum stent diameter (mm) | 3.0±0.4 | 2.9±0.4 | 0.503 |
| Minimum stent diameter (mm) | 2.8±0.4 | 2.6±0.3 | 0.109 |
| Use of post-dilatation balloons (%) | 26.2 | 25.0 | 0.874 |
| Intracoronary ultrasound (%) | 4.8 | 6.2 | 0.858 |
| Other techniques (%) | 0.0 | 8.5 | 0.078 |
| Rotational atherectomy | 0.0 | 3.0 | 0.585 |
| Cutting balloon | 0.0 | 1.2 | 1.000 |
| Tornus catheter | 0.0 | 5.5 | 0.209 |
| Amount of contrast dye (ml) | 286±129 | 284±131 | 0.926 |
| Antithrombotic treatment (%) | |||
| Unfractionated heparin | 95.2 | 85.5 | 0.293 |
| Bivalirudin | 4.8 | 13.9 | 0.119 |
| Enoxaparin | 0.0 | 1.8 | 1.000 |
Among patients undergoing coronary angiography, 13-18% have one or more CTO.7,9 Treatment of CTO constitutes one of the most complex tasks for interventional cardiologists, due mainly to difficulty in recanalizing the vessel, but also to the high risk of restenosis, reocclusion and new revascularization procedures in patients with an initial successful result.1–3 This explains why only about 10% of CTO are scheduled for percutaneous revascularization, and most cases are managed either with medical treatment alone or with surgical revascularization.7,10
Several studies have shown that successful treatment of CTO is associated with improvement in left ventricular ejection fraction and clinical outcomes.3,11 Thus, in spite of the technical difficulties associated with percutaneous treatment of this type of lesion, CTO is currently one of the fields of greatest interest for interventional cardiologists, and consequently a wide variety of devices, recommendations, and techniques have been developed specifically to treat these lesions. As a result, the variability between different centers in the treatment of CTO is greater than with other types of lesions, and therefore data obtained from a single center are difficult to apply to other centers.
The CIBELES trial was performed in 13 centers in Spain and Portugal, in which 207 patients with CTO were randomized to sirolimus- or everolimus-eluting stents.7,8 This study has provided valuable information on how CTO are currently treated. As no specific recommendations were given regarding approach (femoral vs. radial), use of retrograde techniques, types of guidewires, or different devices, the results represent the daily practice of the participating centers. The study has afforded some interesting insights. First, the number of devices used (including balloons, stents, and guidewires) was high, suggesting that the treatment of this type of lesion is expensive and therefore cost-effectiveness analyses of non-CTO lesions might not be applicable to CTO.
Second, the total stent length was high (nearly 50 mm). In some previous randomized studies of patients with CTO, total stent length was less, probably reflecting patient selection.12,13 However, other studies showed a similarly high stent length to CIBELES, which probably reflects the fact that CTO are frequently associated with long-segment disease.4,14
Third, a relatively high proportion of patients did not receive any device, material or technique developed specifically for the treatment of CTO. For example, retrograde techniques were used in only 5% of patients, demonstrating that they have a low penetration in daily practice in Spain and Portugal. In some CTO registries, mainly Japanese, this percentage is around 25%.4 The use of devices recommended by CTO expert groups15 was also relatively low. Microcatheters were used in one third of patients, 34% of patients did not require specific guidewires, and the procedure was guided by intracoronary ultrasound in only 6% (Table 5). In patients with >3 months since vessel occlusion, the use of these devices was slightly more frequent, but also less than expected. On the other hand, the use of a radial approach (frequently not recommended in CTO because it provides less support than a femoral approach) was relatively high (23%), even in patients with duration of occlusion >3 months.15 These data suggest that recommendations by CTO expert groups may not be applicable to the routine treatment of these lesions. However, this does not necessarily imply suboptimal use of resources, but perhaps that the recommendations of these expert groups are unrealistic. All physicians participating in the CIBELES trial were experienced interventional cardiologists with wide experience in the treatment of CTO.
Proportions (mean±standard deviation) of the use of different material, devices, and techniques and variability between participating centers.
| Mean±SD | Variation coefficient | |
| Radial approach | 21±26 | 1.24 |
| Retrograde technique | 5±7 | 1.40 |
| Use of microcatheters | 41±39 | 0.95 |
| Use of post-dilatation balloons | 31±32 | 1.03 |
| Plaque modification devices | 8±8 | 1.00 |
| Intracoronary ultrasound | 7±15 | 2.14 |
| Specific guidewires | 82±30 | 0.37 |
Four, post-dilatation balloons were used in only 25% of patients. This could be considered a low figure, given the expected high proportion of underexpanded and/or malapposed stents in such long stented segments.
Five, other issues, such as the use of other techniques (e.g. rotational atherectomy), antithrombotic treatment, and the amount of contrast dye, were consistent with other CTO series.4,5,16
Finally, due to its study design, all patients included in the CIBELES trial received drug-eluting stents. Recent recommendations on the treatment of CTO do not clearly indicate the routine use of drug-eluting stents in these lesions,15 but we believe that, unless there is an absolute contraindication for prolonged double antiplatelet therapy, all CTO should be treated with drug-eluting stents, particularly with sirolimus- or everolimus-eluting stents.8,12,13,17 In fact, the use of drug-eluting stents was >95% in some recent registries on CTO.4
Study limitationsThis study has some limitations. First, the main objective of the CIBELES trial was to compare two different types of drug-eluting stents, and did not include analysis of the material and techniques used in the trial's endpoints. However, this in fact reinforces the findings related to the techniques and material used: since no specific recommendations were given in the study, the data in this article reflect the daily practice of the participating centers. Second, due to the study design, in all included patients the guidewire successfully crossed the vessel occlusion, and this may have influenced the study's results. However, we believe this may be only applicable to guidewires, and not to other devices used in CTO. Third, the centers participating in the CIBELES trial were only in Spain and Portugal, and treatment of CTO may differ in other countries. Despite these limitations, we believe that the findings probably reflect daily practice in most countries and centers treating CTO, at least in Europe and the USA.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that the procedures followed were in accordance with the regulations of the relevant clinical research ethics committee and with those of the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki).
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data and that all the patients included in the study received sufficient information and gave their written informed consent to participate in the study.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the written informed consent of the patients or subjects mentioned in the article. The corresponding author is in possession of this document.
FundingUnrestricted grant from Abbott Vascular.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Principal investigator: Raul Moreno. Co-principal investigator: Eulogio Garcia. Clinical Events Committee: Esteban Lopez de Sa, Carlos Macaya, Jose-Luis Lopez-Sendon. Investigators: Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid, Spain: Raul Moreno, Guillermo Galeote, Angel Sanchez-Recalde, Santiago Jimenez-Valero, Luis Calvo, Ignacio Plaza, Angela Portela (42 patients). Hospital de Santa Cruz, Lisbon, Portugal: Rui Campante Teles, Manuel Almeida, Luis Raposo, and Pedro Araujo Goncalves (34 patients). Hospital de Galdakao, Bilbao, Spain: Jose-Ramón Rumoroso, Mario Sabada Sagredo, Asier Subinas Elorriaga (28 patients). Hospital de Santo Antonio, Porto, Portugal: Henrique Cyrne Carvalho, Joao Silveira, and André Luz (21 patients). Hospital Puerta de Hierro, Majadahonda, Spain: Francisco Javier Goicolea, and Jose Antonio Fernández Díaz (17 patients). Hospital Virgen de la Salud, Toledo, Spain: José Moreu, and Tomás Cantón (15 patients). Hospital German Trias I Pujol, Badalona, Spain: Fina Mauri, and Oriol Rodriguez (14 patients). Hospital Santa Creu I Sant Pau, Barcelona, Spain: Antonio Serra, Manel Sabate (12 patients). Hospital General, Alicante, Spain: Vicente Mainar and Javier Pineda Nodar (9 patients). Hospital de Santa Marta, Lisboa, Portugal: Lino Patricio, Rui Ferreira (7 patients). Hospital Virgen de la Arrixaca, Murcia, Spain: Mariano Valdés, Javier Lacunza (5 patients). Complejo Hospitalario de León, Spain: Felipe Fernández-Vázquez, Armando Pérez de Prado (2 patients). Hospital García de Orta, Lisboa, Portugal: Helder Pereira (1 patient).