Papillary fibroelastoma (PFE) is a rare primary benign tumor of cardiac origin that predominantly affects the cardiac valves. Although most patients are asymptomatic, serious complications may result given their propensity for embolization. Advances in imaging technology have enabled earlier detection and more accurate characterization of these tumors. We report a case series, describing clinical presentation, treatment and outcome.
MethodsInstitutional records of a tertiary center between 1997 and 2015 were reviewed for all patients diagnosed with PFE treated surgically and confirmed histologically. Demographic and clinical characteristics, echocardiography findings and treatment modalities were analyzed and recurrence at follow-up was studied.
ResultsA total of 26 patients (69% male), aged 54±18 years, had a PFE. Clinically, PFE presented with neurologic deficits in eight cases and was asymptomatic in 65.4%. The mitral valve surface was the predominant tumor location (53.8%), followed by the aortic valve (34.6%). Tumor size ranged between 3 mm and 22 mm, 26.9% had a pedicle and 42.4% were mobile. All patients were treated successfully by complete resection, isolated in 88.5% and with valve repair in three cases. No other cardiac procedure was performed concomitantly and there were no major postoperative complications. Median follow-up was 61±49 months and no tumor recurrence or embolic events were documented.
ConclusionsFibroelastomas are generally small, single and detected by chance during routine imaging exams. Complete surgical resection of the tumor has an excellent prognosis and appears to be a good strategy.
Os fibroelastomas papilares (FP) são tumores benignos primários de origem cardíaca, que afetam predominantemente as válvulas. Embora a maioria dos doentes seja assintomática, podem ocorrer complicações graves por causa de sua propensão para embolizar. A melhoria das técnicas de imagem moderna permitiu a deteção precoce e melhor caracterização desses tumores. É nosso objetivo apresentar a casuística do Serviço, descrever a apresentação clínica, o tratamento e os resultados cirúrgicos.
MétodosForam revistos os dados institucionais entre 1997 e 2015, de todos os doentes com o diagnóstico de FP tratados cirurgicamente, com confirmação histológica. Foram analisadas as características demográficas, clínicas, ecocardiográficas e cirúrgicas. A recorrência durante o seguimento foi também objeto do estudo.
ResultadosForam identificados 26 doentes (69% homens), de 54±18 anos, com FP. O FP apresentou-se com deficit neurológico em oito doentes, nos restantes casos o diagnóstico foi casual. A superfície valvular mitral foi a localização mais frequente (53,8%), seguida da válvula aórtica (34,6%). A dimensão do tumor variou de 3 a 22 mm, 26,9% eram pediculados e a mobilidade estava presente em 42,4% dos casos. Todos os doentes foram tratados com resseção completa, isolada em 88,5% e com reparação valvular em três casos. Nenhum outro procedimento cardíaco foi feito concomitantemente e não se registaram complicações cardíacas major no pós-operatório. O período mediano de seguimento foi de 61±49 meses, não foi documentada recorrência do tumor nem de eventos embólicos.
ConclusõesOs fibroelastomas são geralmente pequenos, isolados e mais frequentemente detetados incidentalmente em exames de rotina. A recessão cirúrgica completa do tumor tem um excelente prognóstico e parece ser uma boa estratégia.
Papillary fibroelastoma (PFE) is a rare primary benign tumor of cardiac origin, accounting for approximately 10% of all cardiac tumors.1 They can occur anywhere on the endocardium, but are more common in the left heart and display a predilection for valve structures, the aortic valve being most commonly affected.2 Although most patients are asymptomatic, serious complications may occur such as acute valve dysfunction or embolization, giving rise to a wide variety of presenting features including neurologic events, acute coronary syndrome and distal embolic events.3–5
Thanks to improved echocardiographic resolution and modern imaging modalities, these tumors are increasingly often recognized. It is therefore possible that the real incidence of PFE is underestimated.6 Clinicians must be able to decide how to manage patients with incidental echocardiographic findings as well as those with symptoms that may be attributed to these masses. Few systematic reviews or comprehensive studies have provided results that validate either a medical or a surgical approach, although in an recent single-center retrospective study, Tamin et al. concluded that patients with echocardiographically suspected PFE who do not undergo surgical removal have higher rates of cerebrovascular accident and mortality.7 Given that there have been no randomized clinical trials aimed at defining the optimal treatment strategy, we decided to review our institution's surgical experience with PFE over an 18-year period. We present our findings and discuss demographic, clinical and echocardiographic characteristics and current treatment approaches along with results of our follow-up assessments.
MethodsWe performed a retrospective review of all patients diagnosed with cardiac PFE who underwent surgical excision at our institution between January 1997 and December 2015. Patients were identified from the cardiovascular surgery and pathology databases. Cardiac PFE was the primary indication for surgery, and therefore patients undergoing heart surgery for other reasons in which the tumor was a additional finding were excluded from our study. Clinical histories, echocardiographic reports, operative notes and histopathologic findings were reviewed. Demographic characteristics including age and gender, clinical data including presenting symptoms, concurrent cardiac disease, comorbidities, tumor location and left ventricular ejection fraction, operative procedures, and follow-up findings were collected. Since all patients with PFE diagnosed pathologically from surgical specimens had at least one transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) and/or transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) leading to the diagnosis, the echocardiographic characteristics of the tumor including location, number, attachment characteristics, movement, size and valvular involvement were also collected. A presumed diagnosis of cardiac PFE by echocardiography was based on its appearance, which is usually of a small, mobile, pedunculated or sessile valvular or endocardial mass that frequently flutters or prolapses into the cardiac chambers during systole or diastole. They may appear speckled with echolucencies and a stippled pattern near the edges, which correlates with the papillary projections on the surface of the mass.8,9
Neurologic events were attributed to the PFE in patients with no concurrent atrial fibrillation and no significant carotid or cardiac disease. Follow-up data were collected from telephone interviews of patients. The endpoints were clinical embolic events, need for further cardiac surgery due to tumor recurrence, or death at follow-up.
Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables. Selected variables were compared between groups by the Student's t test for unpaired data when a normal distribution was demonstrated; otherwise, the nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test was used. Categorical variables are summarized as count and percentages and compared between groups using the Pearson chi-square or Fisher's exact test, as appropriate. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 21 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
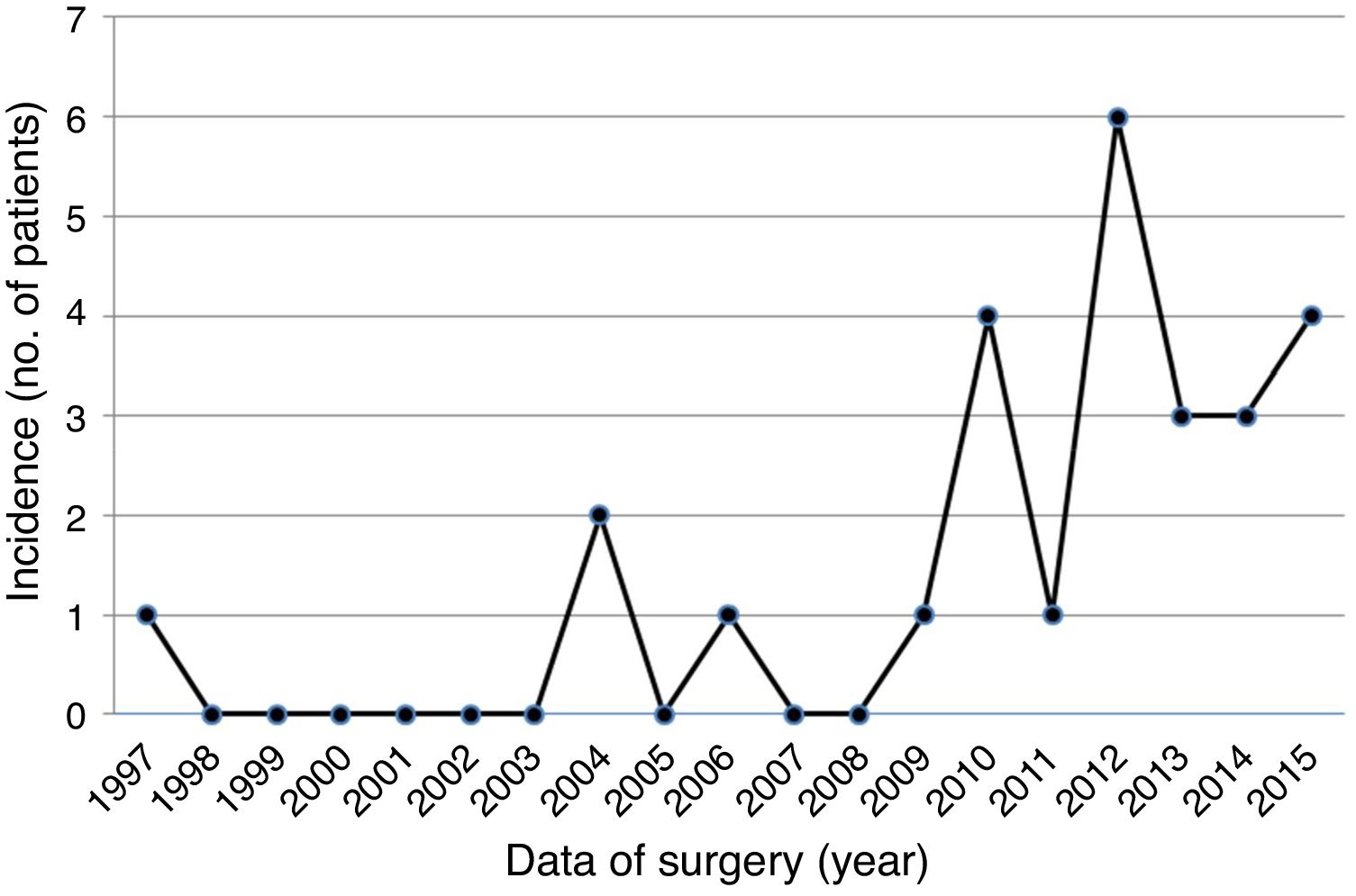
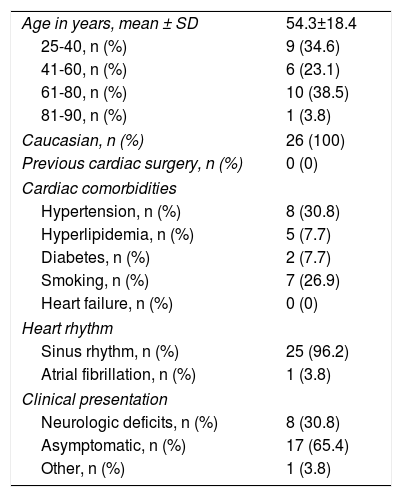
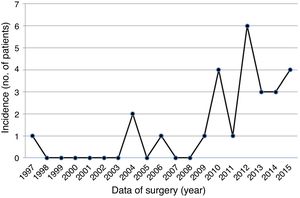
ResultsA total of 26 patients, 18 male (69.2%), mean age 54.3±18.4 years (range 24-88 years), underwent surgical excision of one or more cardiac PFE between 1997 (first record of PFE in our database) and 2015 (Table 1). Over the years, increasingly frequent identification of PFE was observed (Figure 1), with the largest number of cases diagnosed in 2012 (n=6). None of the patients had undergone previous cardiac surgery and the most common cardiac comorbidities were hypertension, hyperlipidemia and diabetes.
Baseline clinical characteristics of the study population (n=26).
| Age in years, mean ± SD | 54.3±18.4 |
| 25-40, n (%) | 9 (34.6) |
| 41-60, n (%) | 6 (23.1) |
| 61-80, n (%) | 10 (38.5) |
| 81-90, n (%) | 1 (3.8) |
| Caucasian, n (%) | 26 (100) |
| Previous cardiac surgery, n (%) | 0 (0) |
| Cardiac comorbidities | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 8 (30.8) |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 5 (7.7) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 2 (7.7) |
| Smoking, n (%) | 7 (26.9) |
| Heart failure, n (%) | 0 (0) |
| Heart rhythm | |
| Sinus rhythm, n (%) | 25 (96.2) |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 1 (3.8) |
| Clinical presentation | |
| Neurologic deficits, n (%) | 8 (30.8) |
| Asymptomatic, n (%) | 17 (65.4) |
| Other, n (%) | 1 (3.8) |
All tumors from the 26 patients included in this report were confirmed histopathologically as PFE following complete excision. In 26 patients, there were 28 lesions; 24 patients had solitary tumors located on valves (Table 2). Tumor size varied from 3 mm to 22 mm (mean 9.9±3.7), 26.9% had a pedicle and 42.37% were mobile. The valve surface was the predominant location, comprising 92.3% of the total, with 53.8% on the mitral valve, followed by the aortic valve in 34.6%, left ventricular wall in 3.8% and right atrium in 3.8%. In one case (3.8%) the aortic valve and left ventricle were simultaneously involved. The majority of tumors arose in the left heart (96.2%). Clinically, PFE presented with neurologic deficits in eight cases (in which echocardiography was performed to exclude a cardiac embolic source), 65.4% were asymptomatic and were identified by routine echocardiography, and in one patient it presented as shortness of breath not directly related to the presence of a cardiac mass. The tumor was thus an incidental finding in most patients.
Echocardiographic features of the study population (n=26).
| Study population, n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Reason for TTE | |
| Routine | 17 (65.4) |
| Exclude cardiac source of embolism | 8 (30.8) |
| Other | 1 (3.8) |
| Location of lesion | |
| Aortic valve | 9 (34.6) |
| Mitral valve | 14 (53.8) |
| Right atrium | 1 (3.8) |
| Left ventricle | 1 (3.8) |
| Aortic valve and ventricular myocardium | 1 (3.8) |
| Number of lesions/patient | |
| 1 | 24 (92.3) |
| 2 | 2 (7.7) |
| Size | |
| <5 mm | 1 (3.8) |
| 5-10 mm | 17 (65.4) |
| 11-15 mm | 6 (23.1) |
| >15 mm | 2 (7.7) |
| Pedicle | 7 (26.9) |
| Mobility | |
| None | 15 (57.7) |
| Low | 6 (23.1) |
| High | 5 (19.2) |
| LVEF >55% | 26 (100) |
LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; TTE: transthoracic echocardiography.
Stroke was the clinical presentation in 30.8% of cases; these patients were younger, aged 42±17 years (p=0.026). Patients with neurologic events had lesions ranging in size from less than 5 mm to 11 mm in diameter, and a pedicle was present in three patients. No other differences were found between these and asymptomatic patients. All these tumors were on the left side of the heart, with 75% on the mitral valve and 25% on the aortic valve. In these cases stroke was considered secondary to tumor embolism.
Of 24 patients with isolated valvular PFE, none had valve dysfunction or other associated cardiac disease, and all had preserved left ventricular systolic function. Standard open-heart surgery under cardiopulmonary bypass was performed in all patients and successful complete surgical resection of PFE was achieved in all cases. In 21 of the 24 patients simple (shave) excision of the tumor was performed, while excision with valve repair was needed in three cases, but no valve replacement. Valve-sparing surgery was thus performed all cases. No other cardiac procedure was performed concomitantly and there were no major postoperative complications. The median postoperative follow-up was 61.4 (range 7-223) months. In self-reported telephone interviews no deaths, tumor recurrence or embolic events were documented.
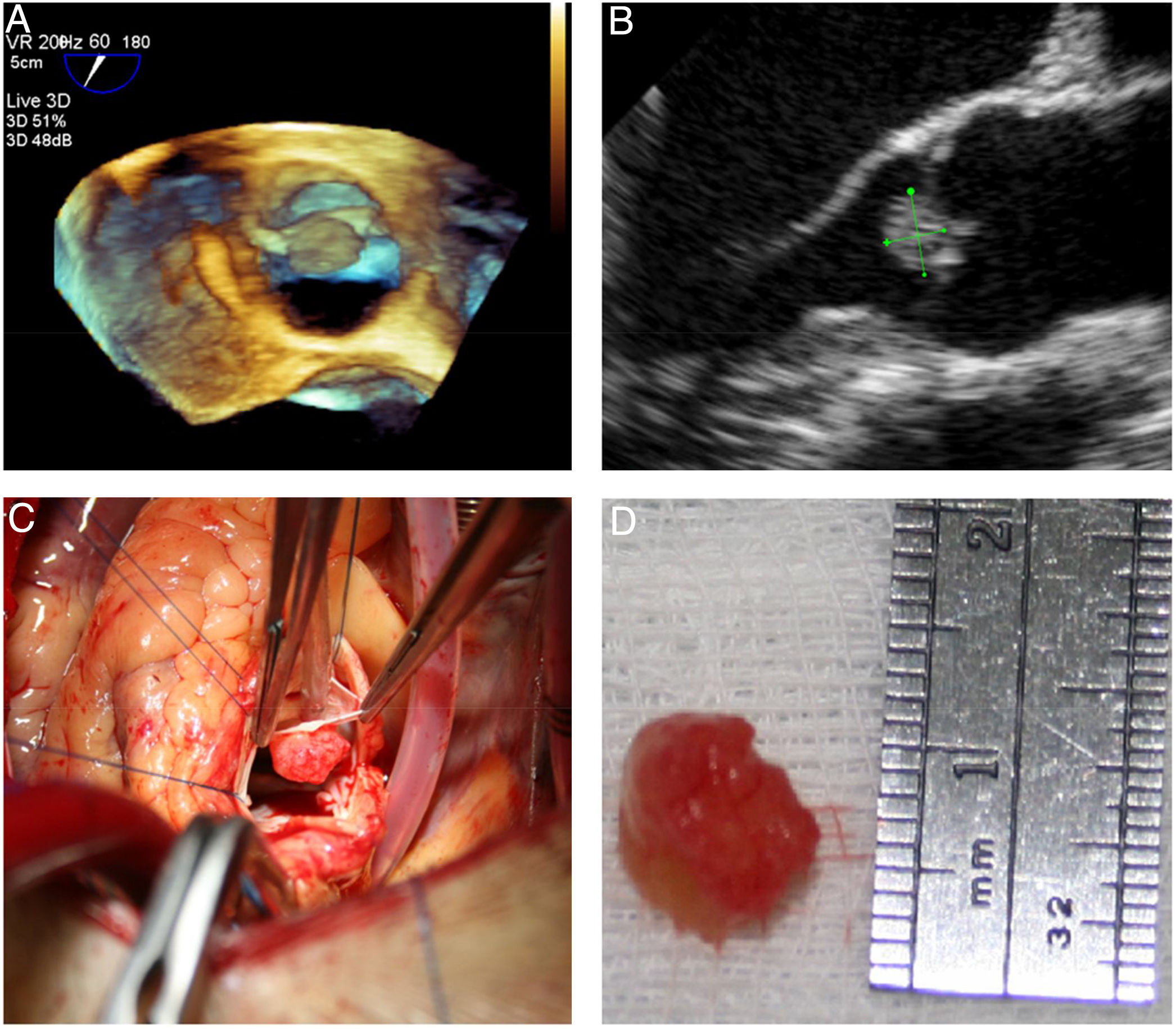
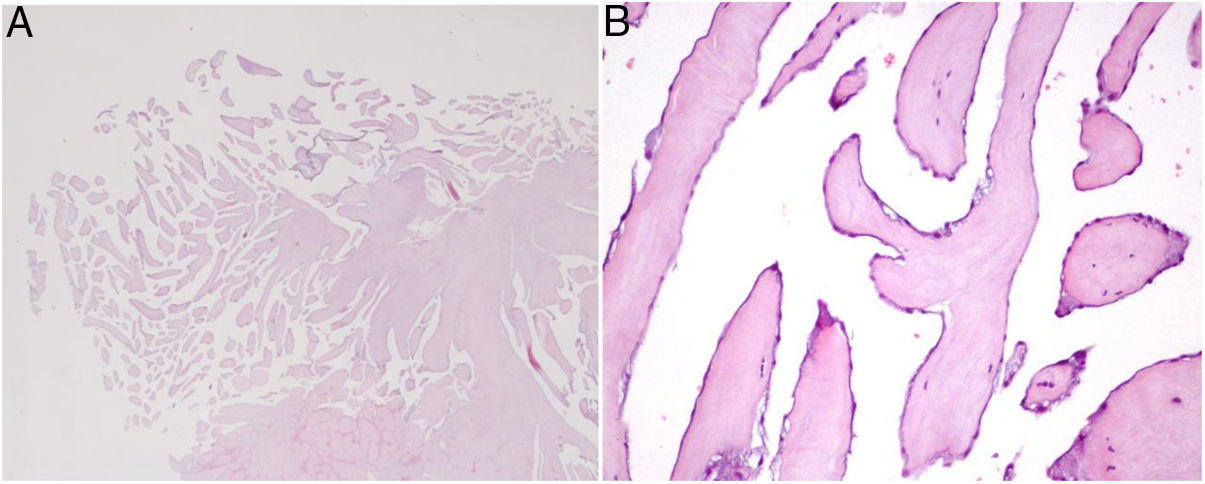
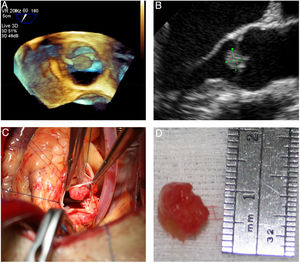
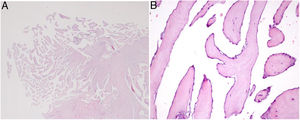
Grossly, PFEs appeared as a single (multiple in only two cases) small mass (the largest was 22 mm in size, found in the oldest patient), with delicate, smooth, white papillary fronds, giving a sea anemone-like appearance when placed in water or saline or a flower-like appearance in situ (Figure 2). Microscopically, the papillary fronds were narrow, slender and branching. These fronds, often prominent, surround a layer of myxoid matrix rich in acid mucopolysaccharide and an inner avascular, paucicellular connective core. The peripheral rim and the core contained coarse and fragmented elastic fibers (Figure 3).
Microscopic appearance of papillary fibroelastoma. (A) Panoramic view of the lesion showing avascular branching fronds lined by endothelial cells (hematoxylin/eosin stain, original magnification ×16); (B) the fronds consist of a fibrous core surrounded by loose connective tissue and an endothelial lining (hematoxylin/eosin stain, original magnification ×100).
Given the low incidence of these tumors and the lack of longitudinal follow-up studies, their natural history remains poorly understood.
Historically, PFE was first described as a “valvular tumor” in 1931 by Yater,10 and the term “papillary fibroelastoma” was introduced in 1975 by Cheitlin et al.11 In the past, most knowledge of cardiac tumors was based on postmortem studies, but nowadays, with modern echocardiography, such tumors are increasingly diagnosed in vivo. In recent years, several articles have been published providing more information on PFE.2,12,13
Macroscopically, PFE are characterized by multiple frond-like fibrous projections creating a sea anemone-like appearance when immersed in saline. Histologically, the tumor consists of an avascular fibroelastic core, made up of a hyalinized collagen matrix with a rim of smooth muscle cells and elastic fibers, lined by endocardial endothelium.14,15 Although its etiology remains largely unknown, several hypotheses have been reported, including fibroblast infiltration with organization of mural thrombi, virally induced tumor growth and an endocardial response to mechanical trauma or radiation damage.16–18
PFEs most often arise from the valvular endocardium. Gowda et al. found PFEs on valvular surfaces in 84% of cases, although they can also appear on the papillary muscles, chordae tendineae, ventricular septum or endocardial surface.2 Although the tumor can be found anywhere within the heart, in our series it was found primarily on cardiac valves, mitral more often than aortic, unlike other studies in which the aortic valve is the most frequent valve location.2,12,13 Most tumors were solitary, less than 10 mm in diameter, and found in older patients. Multiple lesions are uncommon; they may appear in the same location or in different sites (one patient in our series had two tumors on the aortic valve, and the other had one on the aortic valve and one on the left ventricle). A case report documented up to 40 PFE in both ventricles in one patient.19 In our review, echocardiographic features that suggest PFE with a high degree of suspicion are small size (usually <1.5 cm), attachment by a pedicle or stalk to the endocardium, and some degree of mobility. These characteristics are in agreement with published descriptions.8,9
PFE can be incidental discoveries on echocardiograms, computed tomography scans or magnetic resonance imaging. When symptomatic, they can present in a variety of ways, most commonly with cardiovascular symptoms. Most of our patients (65.4%) were asymptomatic; symptomatic cases (30.8%) were most often due to a thromboembolic cerebrovascular accident. Other documented embolic complications include retinal artery occlusion, myocardial infarction, ischemic extremity, and mesenteric ischemia. Others report symptoms resulting from partial or complete obstruction of valves, ventricular outflow tract, or blood vessels, leading to pulmonary edema, myocardial infarction, heart failure, syncope, or sudden death. PFE has also been associated with conduction abnormalities.20
The management of PFE is the subject of debate but mainly depends on its clinical presentation. Surgical excision is recommended in symptomatic patients, regardless of tumor size. Excision is also recommended in patients undergoing cardiac surgery for other reasons. There is still no consensus on the management of asymptomatic patients. Mariscalco et al.21 proposed a management algorithm, selecting characteristics of the lesion other than location as the determinant for intervention. They suggest that mobile lesions, regardless of size, should be surgically excised given the higher risk of thromboembolic complications. Nonmobile lesions less than 1 cm in diameter can be managed expectantly or with anticoagulation. Although thrombi have been reported on the surface of fibroelastomas, there are no guidelines for evaluating the efficacy of anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy in affected patients. Gowda et al. identified 25 patients with presumed PFE who did not undergo surgery and were managed with anticoagulation alone, and who had a poor outcome.2 Although asymptomatic PFE can be managed with close echocardiographic follow-up, we believe that surgical excision is more often prudent given the severity of potential embolization, particularly with left-sided PFE. In addition, recurrence of PFE is very low.12
Although the rarity of this cardiac tumor means there are limited data available, the present study, to our knowledge, includes the largest series of patients with PFE in Portugal.
Study limitationsThis study is retrospective and relies on the database of a single institution to identify patients. Because it is a small series the association with clinical events is based on indirect evidence.
ConclusionsPFE are uncommon tumors of the endocardium, primarily valvular. They are generally small and single but may be multiple and occur on any endocardial surface. Although mostly asymptomatic they can be associated with embolic events, and may cause other cardiovascular symptoms. Their characteristic echocardiographic appearance means they can readily be recognized. Successful surgical resection of valve tumors can be performed and the native valve can frequently be preserved. Management remains difficult because of the rarity of the tumor. Clinical decisions should be individualized and further studies with longer follow-up are needed. Although the optimal surgical approach remains the subject of debate, in light of our center's experience, surgical removal of the tumor by standard median sternotomy is a safe procedure and has excellent medium- and long-term results.
Funding sourcesThere were no funding sources for this project.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
We thank the staff of the Department of Anatomical Pathology of our hospital for their assistance in providing us with the histological images.