A male neonate was born at term. Obstetric ultrasound at 36 weeks showed two hyperechogenic masses, one located in the mid interventricular septum occupying the total thickness of the septum and the other attached to the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve. The baby was born by normal delivery, with a birth weight of 3280 g and an Apgar score of 10 at first minute and 10 at fifth minute. On physical examination, he had a grade III/VI systolic heart murmur best heard at the left sternal edge. An echocardiogram on day one revealed multiple masses with features of rhabdomyomas, located at the apex of the right ventricle, tricuspid and mitral valves, interventricular septum, left ventricular lateral wall and outflow tract. The left ventricular outflow tract mass (15 mm×9 mm) caused a peak gradient of 92 mmHg and a mean gradient of 49 mmHg (Figure 1a and b). The newborn underwent serial clinical and echocardiographic assessment. He remained asymptomatic and the masses underwent progressive reduction. At one month the left ventricular outflow tract mass measured 14 mm×8 mm and at latest follow-up at six months measured 12 mm×8 mm (Figure 2a and b). The peak left ventricle-aorta gradient had decreased to 29 mmHg, with a mean of 13 mmHg, at the last follow-up. A diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis was made by genetic testing, which confirmed a mutation in the TSC-2 gene.
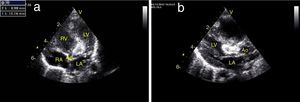
(a) Day one, apical 5-chamber view: a large mass obstructing the left ventricular outflow tract, measuring 15 mm×9 mm; (b) day one, parasternal long-axis view: a large mass almost completely occluding the left ventricular outflow tract. Ao: aorta; LA: left atrium; LV: left ventricle; RA: right atrium; RV: right ventricle.
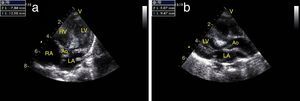
(a) Six months, apical 5-chamber view: regression of the mass obstructing the left ventricular outflow tract, now measuring 12 mm×8 mm; (b) six months, parasternal long-axis view: clear regression of the mass. Ao: aorta; LA: left atrium; LV: left ventricle; RA: right atrium; RV: right ventricle.
A small reduction in the volume of obstructive masses in infants leads to a significant decrease in gradients. Sometimes it is better to wait!
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.