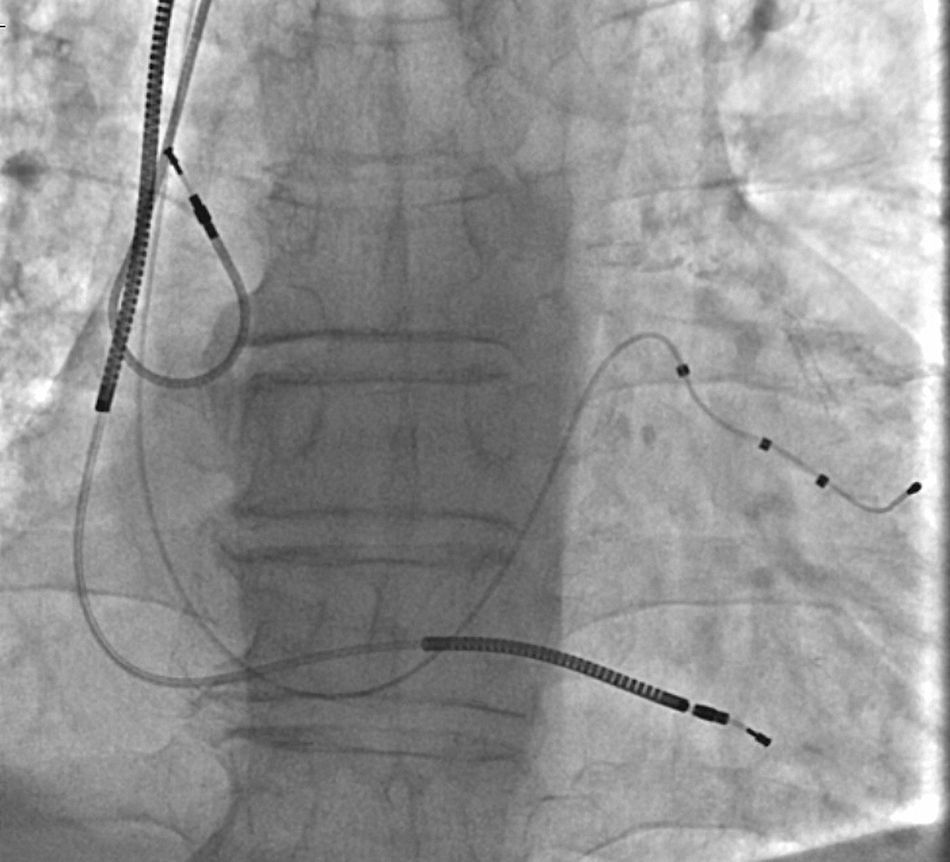
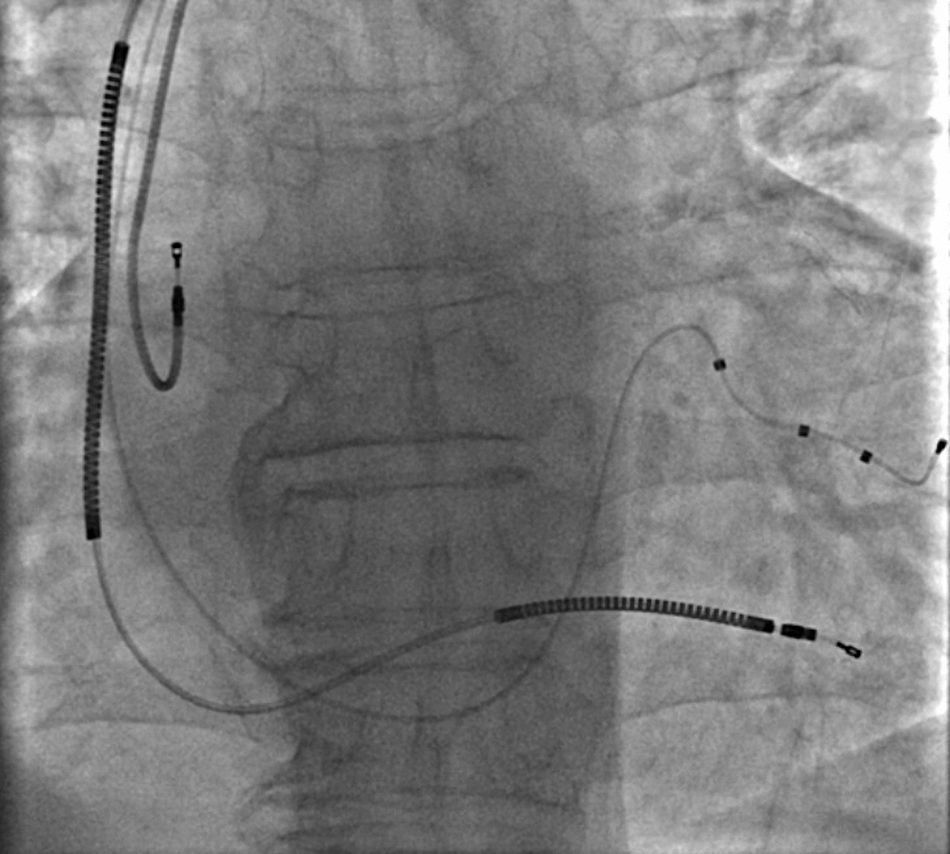
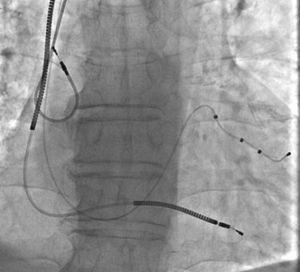
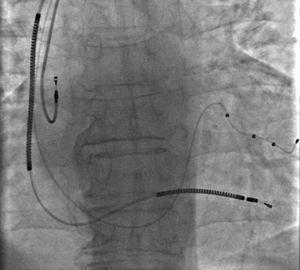
A 67-year-old male patient with ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy underwent implantation of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator with cardiac resynchronization therapy about one month ago. The implantation process was successful and the patient was discharged in good condition. At the routine first month follow-up, pacemaker analysis revealed that there was no atrial pacing and sensing, although the patient was still in sinus rhythm. Angiography showed dislodgement of the J-shaped passive fixation atrial lead to the superior vena cava (Figure 1). Percutaneous transcatheter repositioning of this displaced atrial lead was initially planned before consideration of standard repositioning by reopening the generator pocket. For this purpose, a deflectable ablation catheter was introduced and advanced to the superior vena cava. The displaced atrial lead was then hooked and pulled down to the right atrium, and the lead tip was guided into the right atrial appendage by the deflected ablation catheter (Movie 1, Figure 2). After the procedure, detection of the atrial lead sensing and pacing functions showed they had returned to completely normal. We introduce here a unique percutaneous transcatheter lead repositioning method which has rarely been reported in the literature and is technically very safe and easy. We believe this technique may reduce the need for surgical lead revision and the associated morbidity and cost.
The authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.